1. INTRODUCTION
Social media are a communication phenomenon which is becoming more and more influential in business. Online social media can be defined as ‘’a service based on web which allows individuals to (1) build public or semi-public profile in enclosed system, (2) create a list of users they are linked to and (3) observe and use their own lists of connections and other people’s lists of connections inside the system.’’(Danah and assoc. 2007) . According toKušić (2010) , the central part of social media are Profiles as unique pages where every individual can introduce to others through personal information like age, gender, interests and other, as well as multimedia and applications which personalize and enrich any profile. Social media are becoming the central communication tool especially among younger generations who use it to express attitudes and opinions, share events and create groups with similar interests. The big advantage of social media is the possibility it provides to analyse buyers, their opinions and experiences(Helkkula and Kelleher, 2010) . AsRužić, Biloš and Turkalj (2009) mention, there are over 300 active networks today which share a common goal – to create an image which they will use to present to public via social networking sites.
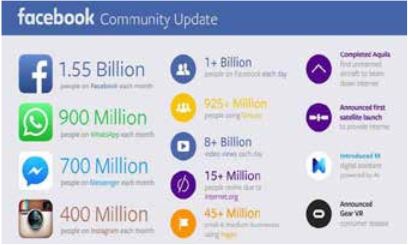
The usage of social media on the worldwide level is as follows: Facebook is the first with over 1, 870 million active users, with 18% market share, 7% more than its rival, WhatsApp – owned by the same owner as Facebook; followed by: Facebook Messenger, QQ, WeChat, QZone, Instagram, Tumbir, Twitter, etc.(Global Social media research summary 2017) .
Since the target population of institutions of higher education is the same population which comprises the majority of Facebook users – the youth, it is clear that this media is largely used in marketing tools of institutions of higher education. Furthermore, if we take into consideration the fact that 55% of users of solely Facebook use it on daily basis, it is clear that this is the most efficient tool for marketing messages to reach the audience (PC Chip, 2017). The influence of Facebook, which has almost two million users worldwide, according to Figure 1, is quite high.
In comparison to older social networking sites like SixDegrees.com, LiveJournal, Friendster, MySpace, etc., Facebook was college oriented. It was created in 2004 as Harward’s online social media and users had to have harvard.edu e-mail address (Newyorker,2015) . In time, Facebook started to include other colleges, high schools, corporations and in the end, everybody over 13 years old(Kušić, 2010) . The statistics show that there were 936 million active users in 2015, 1,440 per month, which proves its popularity(Socialbakers, 2015) .This number has been growing rapidly for years now.
Internet marketing campaign via social media, which is the most common online marketing activity today, requires psychological analysis of users and classifying a target group in order to reach the ‘’right’’ people. Besides analysing users as the first important step, it is also essential to keep constant communication with the group and to interpret feedback from the users in order to implement gained information into the development of online marketing strategy. According to Scott (2010), the fact that it can be focused on specific group of people and that its feedback information, its effects, can be easily evaluated is of great advantage in creating online marketing campaign. Social media are also extremely important in creating good public relations (PR), especially when it refers to external public and generating positive publicity. After a long period of focusing on traditional media, owing to the Internet, public relations have become public relations in its core where organizations have the ability to use different ways to communicate directly with the public via the Internet. The advantage of using social media in marketing campaigns is also evident in increasing return on investment, upgrading consumer acquisition and enabling further recommendations(Zabin, 2009) . Thus, it is obvious why the usage of social media as marketing tool is expanding.
The usage and role of social media is extremely interesting and relevant topic, thus its application in the marketing of education is crucial. By using social media, institutions of higher education can advertise their programmes (as external communication) and work on improving internal communication among its users. However, it is important to analyse how well these institutions are informed about benefits of using this marketing tool and which social media and how often they actually use. This is how current situation can help improve the future situation. Moreover, the aim of this research is to provide an analysis of using social media in institutions of higher education as well as activities of teachers on social media in Croatia as one of the main stakeholders of each institution of higher education. The paper first introduces the concept of social media and analyses its diversity and usage. Furthermore, it shows a detailed overview of usage of social media in Croatia and its usage as a marketing tool in promotion of education. The research conducted among 104 teachers of various institutions of higher education in Croatia analyses their perspective on the frequency of using such media in their institution; which social media are used and if there is a difference in the usage between private and public sector of higher education.
2. SOCIAL MEDIA IN CROATIA
Social media are becoming more and more important every year. The number of active users is growing rapidly and it is estimated that the current number of 2 million users in Croatia will increase in the next few years. From 2,06 million in 2018, 2,1 million in 2019 to 2,18 million in 2022(Statista Report, 2017) .
Currently, Facebook is the largest social network in Croatia. It is used not only by individuals, but also more and more by organisations in order to communicate their messages. Since it is the social media most widely used, we are going to analyse the number of Facebook users in Croatia. The total number of active Facebook users in Croatia is approximately 1,900,000 users; 900, 000 female, 930,000 male. Considering age, most active users in Croatia (58%) are in the age range of 13 and 34 years old. Most of them are teenagers and students (30%), while the lowest number is shown in population over 55 (8%). The distribution is as follows:
13-24 years old – 570,000 users
25-34 years old – 530,000 users
35-44 years old – 370,000 users
45-55 years old – 200,000 users
55-65+ years old - 160,000 users(Arbona, 2017) .
A successful appearance on Facebook has to be well coordinated in advance by strategic plan and its goal has to be creating ‘good atmosphere’ that will spread among users. However, it is important to understand that the content is the key to success. It has to be informative and interesting for the user. If the content is well organized, it expects a reaction from the user which is the biggest advantage of social media – two-way communication. It is essential to follow the results of the posts and campaigns on Facebook, as well as the target group of users in order to adjust future communication.
Besides Facebook as the leading social network, we can identify other social media used in Croatia(Manjgura.hr,2011) , presented in Figure 2.
In 2011 the most popular social media in Croatia was obviously Facebook, followed by Youtube and Twitter. Youtube is the most successful media for exchanging video clips(Xeng,Dale i Liu, 2008.) . Even though it is often mistaken as the service for publishing video clips, Youtube is much more powerful than that. To have a good video which will get more views one does not often need to have a big budget but a creative idea. Twitter is a micro-blogger service restricted to 140 characters and its communication is fast and frequent.(Penović and assoc, 2014) . Twitter owes its popularity to being often used as promotional tool for many movie and music stars or politicians. Even though Twitter has 19,050 registered users in Croatia, only 7,100 are active. Twitter’s value in marketing is in finding influential individuals who can make a campaign viral with minimal funding(Cha, Haddadi, Benevenuto and Gummadi; 2010) .
Instagram and LinkedIn are also showing growth in its popularity in Croatia. Instragram has 390,000 users in Croatia, of which 62% are female. The most common age group is 18-24 year-olds (200,000 users) followed by 25-34 year-olds (100,000 users). Instagram is focused on photographs and it has 200 million users who, on average, spend 257 minutes per month browsing this social media(Market Magazine, 2017.) . On the other hand, LinkedIn is the only social media devoted to individuals and also one of the most visited social media in the world. The most important reason why it is so widely spread is the fact that it provides one place where users can get informed about the news in their industry, form interest groups and have a serious business communication(Penović and sur., 2014.) .
Other growing social media are Google+, Tumblr and Pinterest. Google+ is a network with a high number of users, but this is due to the fact that anyone who logs into any Google service automatically gets Google+ profile. It is important to mention that Google+ users spend on average 7 minutes per month using this media whereas Facebook users spend incomparable 7 hours a week. Tumblr is a platform for creating content which enables users to post comments. Users can follow, share other users’ content on their blogs, mark posts they like, ask questions to other bloggers, etc. An average user spends 1,5 hour per month on this social media. Pinterest is a social media made for sharing visual content, its collecting and sorting. It consists of a profile, theme boards which are filled with ‘’pins’’, i.e. videos. A Pinterest user spends 14 minutes on average per each visit on this social media(Penović i sur., 2014) .
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
A lot of authors has written about the frequency of use of social media in everyday communication between institutions of higher education and potential students as means of creating PR or as a communication tool for students or all participants in such institutions. With the new generation, Web sites become more crucial in order to meet and convince prospective students, who grew up with the Internet(Bozyigit, Akkan, 2014) . One of the Croatian authors isPerišić and associates (2012) who conducted a research on the Polytechnic in Šibenik in order to examine how active students are on social media and whether they find it important as a source of information. It is interesting that, according to this research, 47,8% of students under 24 years of age stated that institutions of higher education should have their own profiles on social media whereas 35,9% of students over 24 share the same attitude.
Hasan Khana’s (2013) research in New Zeland, where he analysed 134 institutions of higher education, showed that institutions of higher education do not give much importance to social media for marketing purposes even though such communication is considered necessary. The reason why social media are not perceived as important is that they are considered unreliable and without clear communicational strategy.
According toRoblyer and associates (2010) social media are communication technologies widely spread among students with the potential to become a powerful resource for students to support their educational institutions. Sometimes institutions of higher education are the ones who fail to meet the needs of modern society, whether it is because of the lack of will or because of uneducated staff in terms of new technologies. Furthermore, the authors indicate that the researches carried out in 2007 by National Centre for Education Statistics showed that teachers were the biggest obstacle in implementing new technologies. Despite that fact, the information used in this research about the usage of social media in online communication of institutions of higher education, is gained from teachers because they are considered as an important part of education as well as the link between institutions and students.
Mazer, Murphy and Simonds (2007) emphasize positive effects of using Facebook in communication of institutions of higher education because all followers, teachers or students, feel like a part of a community and thus become closer. They also point out that if teachers use social media, students perceive that as a positive intention to create link with students.
When observing general usage of e-marketing in everyday communication of institutions of higher education,Bozyigit and Erdem (2014) point out in their research conducted in Turkey that the main tool of social media is its web page. Even though they see room for improvement of web pages of analysed institutions of higher education, they state that 96,7% are connected to social media they actively use. Generally, it can be concluded that the awareness of the institutions about the importance of using social media in marketing communication is increasing. The only question is which social media are used in which locations, i.e. countries. Researches that answer these questions give clear guidelines for marketing practitioners when creating marketing mix of an institution of higher education. The research conducted in Indonesia shows how important Facebook and other social media are in marketing communication. A total of 329 respondents from 2 colleges in Riau had given feedback. The findings show that most of the students had a Facebook account before entering the college (95.14%), spent less than 1 hour per day using it (45.59%) and were logged onto the Facebook several times per day. Furthermore, Facebook provides positive benefits in educational environment, particularly simplifying information sharing as well as file sharing within the group(Erlin and sur, 2015) .
5. METHODOLOGY
4. 1 The instrument studied and procedures
This research used an online survey as an instrument. The link was shared via teachers’ emails throughout Croatia which were available on web pages of institutions of higher education. It was conducted anonymously by an online questionnaire in November 2015, among 104 people. Methods used are correlation analysis, Chi-squared test. SPSS for Windows 22 was used to process and analyse the data. The aim of this research was divided in two separate parts:
First one is to identify how much teachers are aware of activities of their institution of higher education on social media.
The second one was to analyse which social media are used and if there is a study on a degree of usage of specific social media when it comes to private versus public institutions of higher education.
Different social media (Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Youtube, Google +, Instagram and Pinterest ) offered in this online survey are based on practical experience authorsPenović i sur (2014) collected in the book called ”Conquer the Internet or the Internet Will Conquer You” (”Pobijedite internet ili će internet pobijediti vas”) which takes into consideration certain social media as being the most common in Croatian social media market. A scale of possible answers was used concentrating on social media possibly being used by institutions in marketing communication. Thus, the research is based on practical manual and authors’ own perspective on the most often used social media in Croatia. Methodology used in empirical part of this paper can be divided into phases: collecting basic data via survey (questionnaire), collecting additional data online and processing data via different methods: different statistical methods and methods of presenting data via tables and charts (by using Microsoft Excel and SPSS Statistics Software). AsTang (2012) points out, private institutions of higher education are evolving quicker than public ones in every field and thus force public institutions to be more competitive. Also,Bozyigit i Erdem (2014) say that authors(Fuller 1986; Johnes and Taylor 1990 in Wilkinson and Yussof, 2005) in previous researches concluded that it appeared that public universities had better classroom and library facilities, whereas private colleges had superior laboratory and computing facilities. So, it can be concluded that by investing in computing facilities, private institutions also invest in e-communication and e-marketing tools. Therefore, the question is whether private institutions of higher education develop quicker when it comes to using social media in everyday marketing communication.
On account of theoretical part of this paper and the question raised by Tang(Tang, 2012), the hypothesis is:
H1: Private institutions of higher education use social media in marketing communication more intensively than public institutions of higher education.
5. SAMPLE
A questionnaire was sent to teachers working in private and public institutions of higher education all over Croatia. If their addresses were published online, the questionnaire was sent directly and if not, it was sent to institution’s email with a kind request to forward the questionnaire to teachers. 104 replies were received in one week time. Most of the answers were collected in the first two days but the analysis of the results was done seven days later because replies had been arriving at a slower pace throughout these seven days. The questionnaire was sent to all institutions of higher education which had study programmes with content linked to economy, private and public alike. Out of 104 respondents, 82 filled in the questionnaire completely whereas 22 of them answered the questions partially.
5. 1 Results
Teachers were offered a few options of social media – Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Youtube, Google+, Instagram and Pinterest – and were asked about how much their institutions used it, if they used it at all. The overall answers are shown in Figure 3. As expected, teachers perceive Facebook as the most widely used, which is then followed by LinkedIn, Twitter, Youtube, Google + and Instragram. Tumbir and Pinterest are considered not used at all.
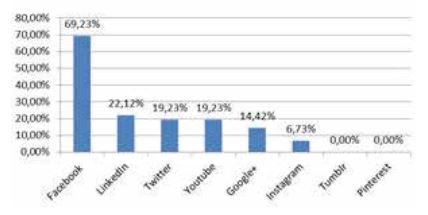
Data source: Authors’ processing
Furthermore, each social media was also studied individually. There is an obvious difference between private and public institutions if we consider the frequency of teachers’ using different social media. The differences will be explained below.
Data source: Authors’ processing
The table shows that, when analysing each social media individually, respondents consider private institutions as more interested in social media generally, but also in each particualr social media. The order of usage in private sector is Facebook, Youtube, LinkedIn and then Google+ followed by Instagram. Public sector shows a slightly different order: Facebook, LinkedIn and Twitter, followed by Youtube and Google+ and finally, teachers consider Instagram as the least used social media in public sector.
Analysing the frequency of using particular social media in Croatia in general, based on theoretical data of this research and comparing it to the use of social media throughout Croatia with answers gained in this research by questioning the teachers, a difference in the order of the level of usage can be noticed. The level of usage of social media in Croatia is derived from given data presented in the paper while the level of using particular social media in a certain institution of higher education is derived from the research done in this paper.
Data source: Author’s processing
Based on the results presented in Table 3, it is clear that there are discrepancies in the perception of using social media in Croatia when analysing higher system of education through attitudes of its teachers.
Furthermore, the level of usage of particular social media is analysed and compared to the results gained in Chi-square test (Table 4).
Data source: Author’s processing
The research results of each individual social network are presented individually. It is obvious that the majority of participants from private sector believe their institution uses Facebook, as well as the participants from public sector believe their institution uses Facebook in everyday marketing communication. It is important to emphasize that between their use there is no significant difference. Next analysed social media was Instagram. It is clear that participants from private institutions believe their institution uses it more intensively that those from public institutions. The analysis of collected data show there is no significant difference between using social media depending on the type of institution of higher education (private or public). The use of other social networks has shown significant difference between participants from private and public institutions.LinkedIn and its usage depending on the type of institution was also analysed. Detailed analysis has shown that statistically, there is a significant difference in using LinkedIn depending on the type of institution (private or public). (Asymp. Sig.=0,002). Additionally, Twitter was also analysed as an everyday informing tool for interested public and its usage depending on the type of institution of higher education. Chi-squared test has confirmed significant statistical difference in using Twitter and also Youtube, depending on the activities of teachers from private or public institutions. Also, Chi-squared test has confirmed significant statistical difference in using Google+ depending on the activities of teachers from private or public institutions.
6. CONCLUSION
Many researches have shown that the majority of users of social media are students or those who are going to become students. Consequently, social media are crucial tool of marketing communication for educational institutions. In their research, the authorsErlina, Fitria and Susandria (2015) mentioned as much as 95,14% Facebook users who already had profiles when applying for university. 45,59% of them log in their profile a few times a day. Many authors wrote about the importance of social media in everyday life as well as in students’ lives.Roblyer and assoc. (2010) are one of those and they warned against institutions of higher education and their teachers who do not follow trends concerning social media even though the number of students using social media is growing rapidly. Some teachers do have their social media profiles, like Facebook, but they only use it for private purposes. However, possibilities are endless; from attracting new students to strenghtening links with head institutions, spreading information, etc. Thus, it is extremely important that teachers, who often represent their institution, accept the challenge and start being active on social media. In this article, authors have analysed the importance of social media in general and in the context of institutions of higher education. The authors have presented an overall usage of certain social media on global and local scale in Croatia. They have also analysed different ways of using social media as a communication tool in institutions of higher education. Furthermore, the research results have shown how much teachers are informed about social media usage in their institution – private or public. Finally, the difference between private and public institutions of higher education in terms of using social media have been analysed. Based on the results presented in Table 2, it is clear that the order of usage of social media in Croatia, regardless of the sector, cannot be applied to the higher education system. Also, it can be concluded that, by refering to teachers’ answers, private institutions of higher education generally use social media more often and they use each social media more often than the public ones.
However, Chi-squared test in this research has shown that there is no significant difference in the usage of the most popular social media like Facebook and Instagram whereas there is a difference in the usage of other social media. Even though private institutions of higher education push public ones to be better and thus together they make headway(Bozyigit i Erdem, 2014) , still private institutions of higher education in this research show faster growth and quicker implementation of changes(Tang, 2012) . Therefore, H1 hypothesis is confirmed. This research can help implement specific marketing communication of institutions of higher education. It is clear that the biggest number of users in Croatia use Facebook so it is logical to invest primarily in this social media. Secondly, Youtube should be regarded as the next step followed by Instagram and others. Even though this research has its limitations like the range of respondents being only teachers and not all participants of higher education, it still gives us indications for further practical implementation. The limitation can also lie in the fact that teachers do not have the real image of what is being done in their institution. In that case it is important to work more actively on internal marketing and communication within the institution. It is quite clear that there is a significant room for improvement of online marketing communication and that the level of usage of social media in Croatia can give us guidelines on which social media to use more often than others.