1. INTRODUCTION
The propulsion of supersonic vehicles, such as fighter jets and missiles, relies heavily on the use of expansion-deflection (E-D) nozzles, which are crucial for enhancing thrust and efficiency. These nozzles are designed to increase the velocity of exhaust gases by converting thermal energy into kinetic energy. The development of supersonic E-D nozzles in the 1950s and 1960s was motivated by the growing need for fighter jets with higher speed and manoeuvrability. Supersonic E-D nozzles employ unique profiles that generate an expansion zone, enabling exhaust gases to expand and thereby enhance their velocity. These nozzles have a similar contour profile to conventional nozzles, but they feature a "central body" located at the throat that redirects the flow towards the wall[1]. The central body directs the exhaust gases further outwards compared to contour profile nozzles, which leads to a significant reduction in nozzle size compared to conventional nozzles with the same area ratio. In an E-D nozzle, the flow adapts to the pressure that arises behind the central body. The E-D nozzle is preferred when a nozzle with a very high area ratio is required, as it is more compact and shorter compared to other nozzle types. The small combustion chamber of the E-D nozzle offers various advantages in terms of cooling requirements and weight[2].
The performance of linear expansion-deflection (E-D) nozzles compared to conventional convergent-divergent (CD) nozzles has been the subject of several studies. In 1960 Rao presented a detailed analysis of the E-D nozzle concept, highlighting its advantages over conventional nozzles in terms of weight, size, and performance[3]. Schomberg et al. conducted several studies showing that the E-D nozzle configuration can improve thrust efficiency compared to conventional designs, even under highly over-expanded flow conditions[4]. Wasko examined the performance of two nozzle types, including E-D nozzles, and found that E-D nozzles had comparable performance to CD nozzles[5]. In their experiments, Schomberg et al. compared a linear variant of the E-D nozzle with a CD nozzle and found that the E-D nozzle exhibited a higher thrust coefficient over the entire range of tested pressure ratios[6]. They also found that the CD nozzle exhibited unstable asymmetric flow separation, while the E-D nozzle had attached flow[1]. Taylor and Hempsell presented an integrated methodology for the design and performance evaluation of E-D nozzles, which involves using numerical fluid dynamics, characteristic methods, and a semi-empirical model to thoroughly analyse the closed flow field of the nozzle[7]. According to the results, the parameters of the throat region play a crucial role in the successful implementation of the E-D nozzle. However, the research findings also indicated that a careful design of the nozzle can lead to a significant weight reduction. Choi and Huh analysed the performance of E-D nozzles with different inflection angles of the tip, depending on the nozzle pressure ratio, for space launch vehicles. The results showed that the nozzle configuration can form an open or closed drag that can be utilised for altitude compensation[8].
The present study focuses on the development of an E-D nozzle profile and the evaluation of the effects of the central body radius on the internal flow behaviour of the nozzle and overall efficiency. ANSYS-Fluent software was employed to compare the performance of the E-D nozzle to a TIC nozzle having the same area ratio.
2. DESIGN METHOD OF AN E-D NOZZLE
The theoretical method is based on simple wave flow concepts described by T.L. Dymond[9]. The program described in this report is simple and provides a scheme for designing the contour of the E-D nozzle. The Prandtl-Meyer relation allows the calculation of the total flow turning angle by using the following equation:
(1)
where is the heat capacity ratio and is the Mach number at the exit.
The relations for the throat gap can be derived from the geometry depicted in Figure 1, as follows:
(2)
(3)
(4)
where is the throat radius, is the central body radius, is the width of throat gap on pure expansion central body and is the angle between the axis and the sonic line.
The surface area of the Prandtl-Meyer expansion wave, after being revolved around the plug axis at the throat, is given by:
(5)
or:
(6)
where is the expansion ratio and is the radius at the exit.
By solving the dimensionless parameter, in Eq. (6):
(7)
where .
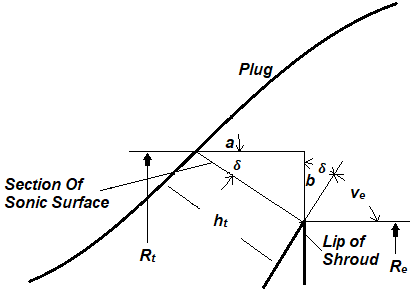
Fig. 1 E-D Nozzle Throat Configuration[9]
This calculation procedure is used to determine the plug contour. It involves incrementally increasing the Mach number on the plug surface from at the throat to at the tip using regular increments of :
(8)
(9)
where is the number of contour points computed on the nozzle wall.
The area of the revolved expansion wave is given by:
(10)
where is the ratio between the radius of point x and the radius of the shroud and is the coordinate of point .
Based on the geometry presented in Figure 2:
(11)
where is the angle between the plug axis and the Prandtl-Meyer expansion wave.
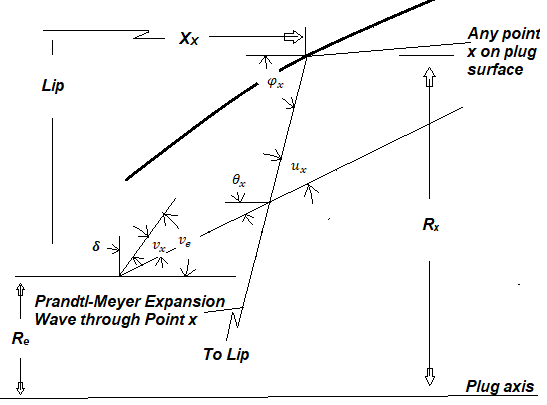
Fig. 2 E-D Nozzle[9]
By solving Eqs. (10) and (11), it is possible to obtain:
(12)
From the geometry presented on Figure 2:
(13)
where is the Prandtl-Meyer and the Mach angle at .
By substituting of Eq. (13) into Eq. (12):
(14)
The mass flow through the revolved expansion wave is given as:
(15)
where , and represent the density, cross-section, and velocity, respectively, at position .
The mass flow through the throat is:
(16)
The mass flow through these two sections should be equal; therefore, can be determined as follows:
(17)
Equations (14) and (17) are then solved for :
(18)
Once the value of is determined, can be calculated based on the geometry presented on Figure 2 using Eq. (19):
(19)
3. DEVELOPMENT OF A FORTRAN PROGRAM FOR THE DESIGN OF THE E-D NOZZLE PROFILE
To facilitate the design of the E-D nozzle profile, a FORTRAN program with flow chart presented on Figure 3 has been developed. The program requires the following inputs: the number of contour points, the radius of the internal circular arc contour, the estimated Mach number, the gas constant and the radius at the exit. The outputs of the program include the Mach number distribution, the coordinates of the nozzle contour and the pressure ratio at each point.
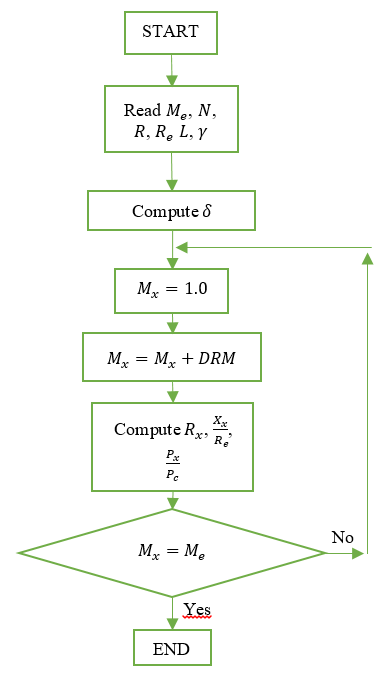
Fig. 3 Flow chart of E-D nozzles design[9]
In Figure 3 is the gas constant and is the ratio of the pressure at point x to the chamber pressure.
4. RESULTS AND INTERPRETATION
Figure 4 shows the computer-generated profile of the Ideal nozzle (in red) alongside its mesh (in green), which was created using our computer code with 50 contour points. The schematic representation of the flow field in the vicinity of an E-D nozzle is shown in Figure 4. The flow within the E-D nozzle consists of three distinct regions. The transition region highlighted in green represents a simple wave region whose solution can be determined analytically. The triangular region corresponds to a parallel, uniform flow with a straight characteristic, which is characterized by an exit Mach number . In the rectangular region, the flow behind the object does not smoothly dissipate into the surrounding air, but forms a recirculating or turbulent region.
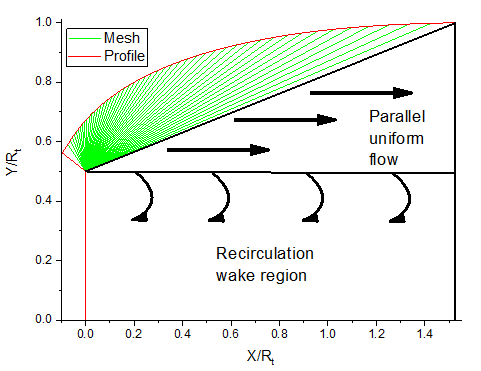
Fig. 4 The obtained E-D nozzle contour for and its mesh
As shown in Figure 5, the Mach number in the divergent section of the nozzle increases continuously until it reaches the design value at the exit. It can be observed that the Mach number at the outlet of the E-D nozzle is . This trend is accompanied by a sharp decrease in the wall pressure ratio (as depicted in Figure 6), which drops to at the edge of the nozzle.
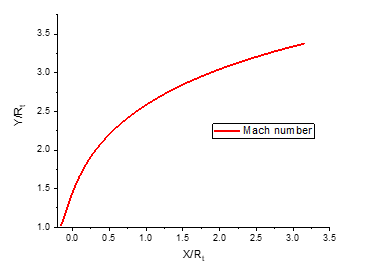
Fig. 5 Mach number evolution along the wall
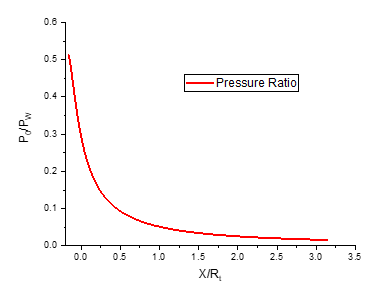
Fig. 6 Pressure ratio evolution along the wall
5. NUMERICAL SIMULATION
In this section, a numerical investigation was conducted to analyze the flow through the E-D nozzle. For spatial discretization, a least-square cell-based gradient approach was used, and the solution was assumed to vary linearly. Additionally, a second-order upwind scheme was implemented for the interpolation of values such as pressure, momentum, turbulent kinetic energy, specific dissipation rate, and energy. For the steady-state computational analysis, the initial solution was determined using full multigrid (FMG) initialization and the inlet boundary was set as the reference value. The viscosity of the air was calculated using the Sutherland equation. The convergence of the solution procedure was checked using the residuals, and the calculations were stopped when the residuals stabilized and fell below the threshold value of .
5.1 Methodology
The analysis of the flow for the E-D nozzle was performed with ANSYS Fluent. A finite volume Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) solver was used. The k-ω SST model is used as the turbulence model, and the system of equations is closed with the equation of state for ideal gas.
5.1.1 Governing equations
The underlying equations are as follows.
The equation for the conservation of mass, or continuity equation, can be written as follows:
(20)
The conservation of momentum is given by:
(21)
where is the stress tensor. The stress tensor is given by:
(22)
where is the molecular viscosity, is the unit tensor, and the second term on the right-hand side represents the effect of volume dilation.
The energy equation is thus given as follows:
(23)
where is the total energy per unit mass (including internal energy and kinetic energy), is the heat flux vector.
5.1.2 Computational domain and boundary conditions
Figure 7 provides an overview of the boundary conditions used in the calculation model. Similar boundary conditions were defined for all geometries investigated. The same boundary conditions are used for different test cases, with the values assigned to the inlet and outlet variables changed to account for low altitude operation and high-altitude operation mode. When analysing E-D nozzles of the Inlet Pressure must be considered as the main inlet boundary condition, while the Outlet Pressure and Wall conditions, particularly an adiabatic wall, serve as key outlet boundary conditions. Together, these parameters determine the behaviour of the fluid as it passes through the nozzle.
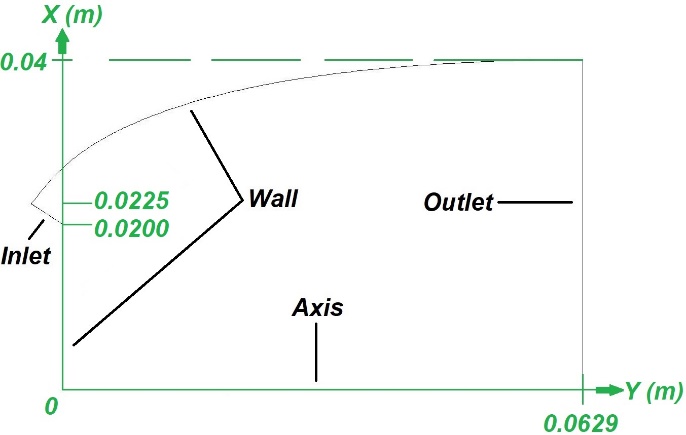
Fig. 7 Numerical computation domain and boundary conditions
The selection of a suitable mesh is a critical phase in numerical simulations. Once the geometry is defined, the choice of a suitable mesh is crucial for the effective solution of the problem. Different mesh sizes are used to evaluate the mesh independence of the results. With the mesh shown on Figure 8, a mesh - independent solution was obtained. In particular, the meshes are refined in the throat region and near the wall, where the local flow properties change rapidly. Figure 8 illustrates a monobloc structured mesh of the nozzle geometry generated in the Ansys-ICEM environment. The mesh comprises a total of 30,351 nodes distributed along the perimeter of the profile, composed of 30,000 quadrilateral cells.
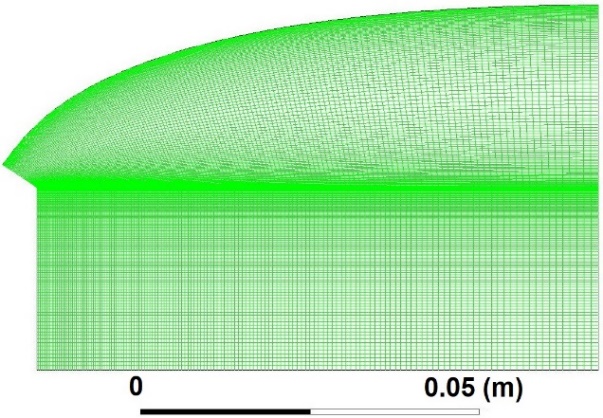
Fig. 8 Structured mesh of the nozzle
5.1.3 Turbulence model
Previous studies have shown that the k-ω SST model is very effective. In a study conducted by Hunter[10], in which different turbulence models were compared in terms of their ability to predict shock waves and their location, the k-ω SST model was found to be the most accurate in terms of experimental results. Perrot[11] also confirmed the accuracy of the k-ω SST model in predicting the distribution of wall pressure and the point of detachment, which closely matched the empirical results. In terms of improved models, Tandra[12] has proposed a modified k-ε model that incorporates three additional terms to enhance its predictive capabilities. Experimental validation has demonstrated that the modified model is able to accurately predict the mean properties of an axisymmetric jet when it is free-flowing, propagating between walls, and impinging on a solid object. Specifically, the performance of the model has been confirmed by experimental measurements that include the prediction of the impact pressure for a supersonic jet propagating between smooth walls. To achieve these results, the k-ω SST model was used as the turbulence model. For the solver in this study, the double-precision density-based coupled solver with Implicit Time Integration was chosen as the baseline. As for the high-resolution scheme, Harten[13] investigated the use of an implicit unconditionally stable high-resolution TVD scheme for steady-state calculations. Belonging to a one-parameter family of second-order accurate explicit and implicit schemes for solving one-dimensional hyperbolic conservation laws, this scheme has been evaluated and demonstrated to have a fast convergence rate and generate a highly resolved approximation of the steady-state solution, without introducing spurious oscillations. The method was used for the compressible inviscid equations of gas dynamics in one and two dimensions. The effectiveness and accuracy of the scheme in the simulation of fluid flows containing shocks was demonstrated by numerical experiments.
The first mesh point near the wall must be in the viscous sublayer. To achieve this, must retain a value around 1 near the wall. The value is from the interval .
5.2 Throat radius effect
To assess how the throat radius affects the flow behaviour and effectiveness of the E-D nozzle, we created four different configurations with a program that uses the equations described previously. The specific radius of the throat and exit for each configuration are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 The radius of the nozzles
Figure 9 shows the nozzle profiles generated by developed algorithm. The geometric and thermodynamic parameters selected for the program are , , and . It can be observed that the length of the nozzle decreases as the throat radius increases. This indicates that the throat radius is a crucial parameter to be considered when analysing E-D nozzles and improving their performance.
The boundary condition values for all geometries listed are as follows.
A total pressure of 5400000 and a total temperature of 330 K were specified at the nozzle inlet. The nozzle walls were set as adiabatic and assumed to be hydraulically smooth. At the outlet boundary, the total ambient pressure of 81675 Pa is used.
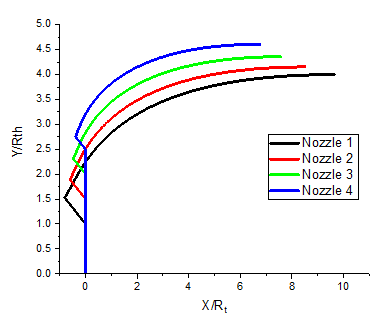
Fig. 9 Nozzle profile
Figure 10 illustrates the change in the Iso-Mach number for each of the four nozzles.
When examining the behaviour of the different nozzles, especially the nozzle with the smallest throat radius (nozzle 1), it is interesting to observe that it operates in closed mode even before the external pressure reaches the critical transition pressure. This indicates an increased sensitivity or responsiveness of nozzle 1 to pressure changes. Nozzle 2, which has a slightly larger throat radius, also shows a closed-mode behaviour, but the onset is delayed compared to nozzle 1, indicating a less pronounced response to pressure changes.
Surprisingly, nozzle 4, which has similar external conditions to nozzles 1 and 2, behaves differently when operating in the adapted mode. The adapted mode indicates a more flexible response to pressure variations, possibly due to differences in design or structural characteristics. This divergent behaviour of the nozzles under the same conditions underscores the importance of throat radius length as a critical factor in nozzle functionality.
Essentially, these results emphasize the nuanced influence of throat radius length on nozzle performance. The results suggest that variations in throat radius contribute significantly to the operational modes of the nozzles, shedding light on the intricate dynamics associated with their functionality under varying external pressures.
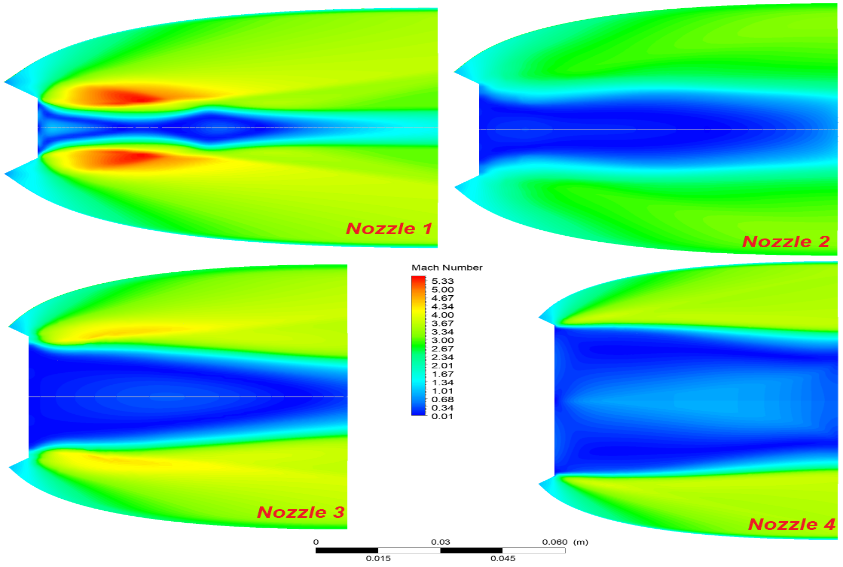
Fig. 10 Iso-Mach number for different configurations
The pressure distribution along the four nozzles is shown in Figure 11. A two-stage pressure drop can be observed in all four nozzles. First, the pressure in the initial expansion zone near the passage drops rapidly until it reaches a certain value. Thereafter, the wall pressure remains constant along the wall.
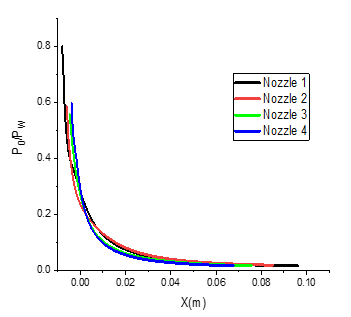
Fig. 11 Wall pressure ratio
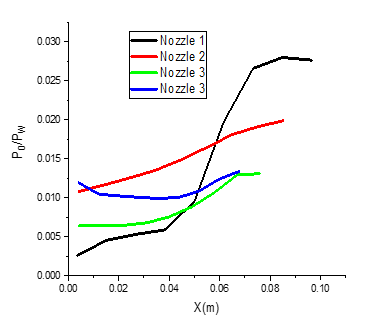
Fig. 12 Axis pressure ratio
Figure 12 shows the pressure distribution along the x-axis for the four configurations. There is a considerable variation in pressure changes from the inlet to the outlet of nozzle 1, which has a throat radius of . Nevertheless, this disparity decreases as the radius increases. For Nozzle 4, which has a throat radius of , the pressure is almost constant along the entire axis. It can be concluded that the radius of the central body has a significant influence on the flow inside the nozzle and these results can contribute to the optimization of the design.
The geometric data of the four configurations are listed in Table 2. It has been shown that the length of the nozzle, the wall area and the thrust force decrease with increasing radius .
Table 2 Geometrical data and thrust
Without the use of controlled flow separation mechanisms, the nozzle of the ED adapts to any altitude. The ambient pressure regulates the exit region of the nozzle in the open wake mode (Figure 13-a), and the exhaust gas does not completely fill the nozzle. The peculiarity of the adaptation of the E-D nozzle to its external environment lies in the use of ambient pressure, unlike other advanced nozzles such as the dual bell nozzle which uses its two bells (the primary bell and the extension) to adapt to the external environment[14, 15]. In closed wake mode (Figure 13-b), the entire exit area of the nozzle is filled by the exhaust gases. The E-D nozzle has two different operating modes, namely the "open wake" mode and the "closed wake" mode. The transition from the "open wake" state to the "closed wake" state occurs when the ambient pressure reaches the design pressure of the nozzle. If the ambient pressure is lowered further, then the remaining expansion would occur outside the nozzle as with a bell nozzle, and the altitude compensation is of no use in this case. The nozzle pressure ratio (NPR) is the ratio of the air jet pressure to the ambient pressure near the nozzle exit.
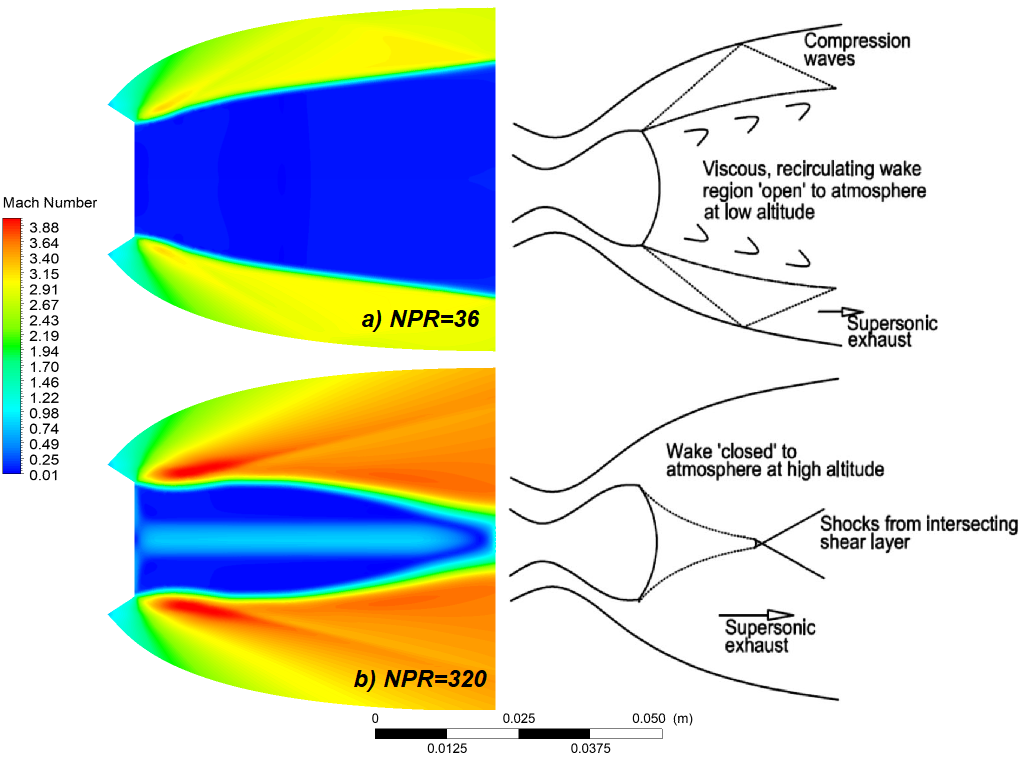
Fig. 13 Iso-Mach contours for E-D nozzle
5.3 Comparison with a TIC nozzle
In this part of the study, a comparative analysis of the E-D and TIC nozzles[16] is performed, based on their equivalent surface area ratio, weight and thrust performance. All geometries are analysed under identical boundary conditions. When comparing the profiles of E-D and TIC nozzles, as shown in Figure 14 and presented in Table 3, it was found that with an equivalent area ratio of , the length of the E-D nozzle is 0.07492 m while the TIC nozzle was longer with a length of 0.0883 m. This means that the length of the E-D nozzle is 15.15% less than that of the TIC nozzle. As a result, the E-D nozzle is more compact and requires less space. To determine the weight of the two nozzles, their surface areas were calculated. The surface area of the TIC nozzle is 0.011483 m2 and that of the E-D nozzle is 0.012592 m² + 0.000224 m², which results in a slight increase in weight.
Variables and , represent the throat area and exit area, respectively. The TIC nozzle profile is determined using the inverse method of characteristics if the boundary conditions at the inlet (transonic domain) and on the centreline are known.
Table 3 summarizes the characteristics of the base nozzle. Figure 14 illustrates the two nozzle configurations, TIC and E-D.
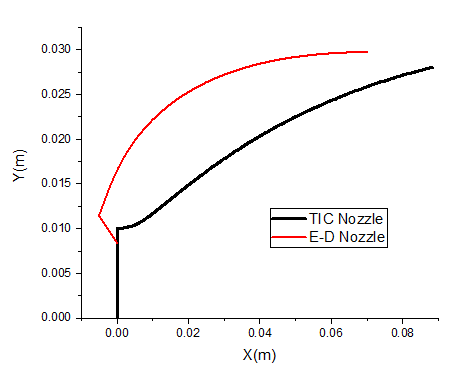
Fig. 14 ED and TIC Nozzle profile
Table 3 Geometric characteristics for both nozzles
| E-D nozzle | TIC nozzle | |
|---|---|---|
| Length ( ) | 0.0883 | 0.07492 |
| Wall area ( ) | 0.012592 | 0.011483 |
| Central body area ( ) | 0.000224 | / |
| Exit radius (m) | 0.02976392 | 0.028 |
In order to investigate the influence of the variation of the nozzle pressure ratio (NPR) on the operating mode of the two nozzles, several nozzle simulations were performed in different operating modes. Figure 15 shows the wall pressure variation according to NPR. To ensure the accuracy of the simulation results, a constant gauge total pressure was used while the ambient pressure was altered as shown in Table 4. Therefore, the underlying physics of the problem under investigation were faithfully reproduced.
Table 4 Boundary conditions values
| E-D and TIC nozzle | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gauge Total Pressure (Pa) | 5400000 | |
| Supersonic/Initial Gauge Pressure (Pa) | 3163320 | |
| Total Temperature (K) | 330 | |
| Pressure outlet (Pa) | 837209 | 10000 |
Figure 15 shows the variation of the Iso-Mach number for both nozzles at NPR=6.45 and 540. At NPR=6.45 (overexpansion), it can be observed that the flow adheres to the walls of the E-D nozzle, in contrast to the TIC nozzle, where flow separation occurs at the walls. Consequently, side loads occur, which lead to a lower efficiency of the nozzle[17, 18].
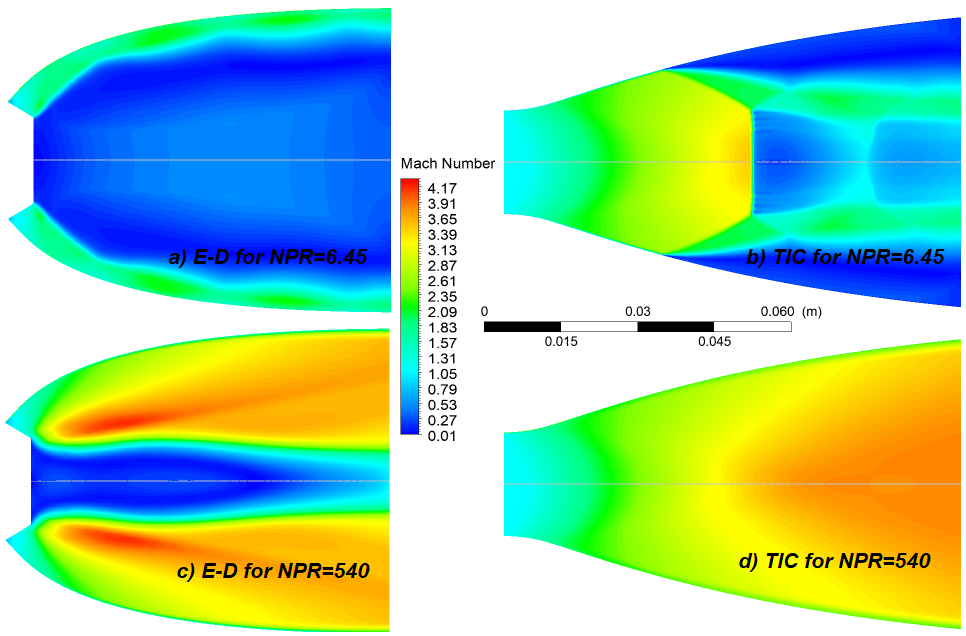
Fig. 15 ED and TIC for different NPR
At an NPR of 6.45 and 540, the E-D nozzle generates a thrust of 688.69 and 2906.19 N, while the TIC nozzle produces a thrust of 599.34 and 2970.51 N. It can be observed that for NPR=6.45, the E-D nozzle provides a significantly higher thrust than the TIC nozzle, with an estimated difference of 12.97 %. However, for NPR=540, the thrust produced by both nozzles is almost equal. This can be attributed to the identical area ratio of the two nozzles.
6. CONCLUSION
The aim of this study is to design an E-D nozzle profile and to analyse the influence of the radius of the central body on the flow behaviour within the nozzle and its efficiency. The results show that an increase in the central body radius leads to a reduction in the length of the nozzle, its wall surface area and the thrust. In the second part of the study, the results of the E-D nozzle were compared with those of a TIC nozzle with the same area ratio of . The lengths determined for both nozzles are 0.07492 m and 0.0883 m, respectively. Therefore, the E-D nozzle is 15.15 % shorter than the TIC nozzle, which has an effect on its weight. When examining the flow in the two nozzles under over expanded conditions, it was found that the flow inside the E-D nozzle adhered completely to the walls, while in the TIC nozzle, a detachment of the flow from the walls was observed. Furthermore, the E-D nozzle produces a significant thrust compared to the TIC nozzle, with an estimated rate of 12.97 %.
To improve subject research, it would be possible to extend the study by incorporating fluid injections into the throat and central body of the nozzles to improve their performance in different operating modes[19]. Furthermore, as a perspective for this study, it would be appropriate to investigate the consequences that may result from varying the nozzle radius beyond the range established in our research, particularly between 0.01 and 0.025.
