1. INTRODUCTION
Garlic (Allium sativum L.) is an important bulbs crop worldwide, with a total production of 26.573.001 t (FAOSTAT database, 2016,http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home). It is still under represented in the Croatian vegetable production, although there is significant demand for this crop. According to the TISUP 2017 (www.tisup.mps.hr), garlic was cultivated in Croatia on about 3.000 ha with the average yield of 3.000kg/ha. However, the average yield of garlic is very low as compared to other leading countries due to many factors. One of the main limiting factors for garlic production is weed infestation, since weeds pose one of the most serious threats to this crop. Many researchers have reported garlic poor competition ability (Carlson and Kirby, 2005,Smith et al., 2008). Weeds compete with garlic for light, nutrients, water and space (Qasem, 1995). They are also host plants of several harmful insects and pathogens (Mishra et al., 2014,Zewde et al., 2007). Also, being a closely planted crop with very small canopy, non-branching habit, sparse foliage and shallow root system, garlic requires frequent irrigation and high fertilizer application that aid to variation in weed species and its abundance (Sahoo, et al., 2018). Moreover, according toZimdahl (1980), garlic can tolerate weeds only up to three weeks after seedling, whileGarcia et al. (1994) reported that economic threshold occurred from 61 to 74 days after transplanting during which time the crop must be kept weed free to maximize bulb yields. In Croatia, most of the farmers depend on manual labor for weeding garlic crop. This traditional method on small family farms include preparatory land tillage, hand weeding by hoe and hand pulling. The alternate method is the use of herbicides. However, weed management methods best suited for an individual grower should depend on several factors such as present weed species, crop variety and stage of growth of the crop, labor costs and availability (Bell and Boutwell, 2001.). Therefore, this study has been conducted to evaluate adequate weed management practice with the best agronomic yield and best economic benefit to the small and medium scale farmers.
2. MATERIAL AND METHODS
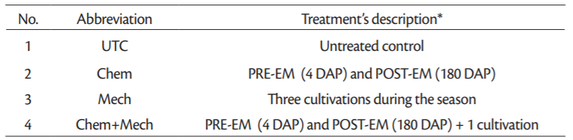
A field experiment was conducted at OPG (Family farm) Maletic situated in Brsadin village in Vukovar-Srijem county (Northeastern part of Croatia) during the 2018/19 growing season. This is an open and flat region with a warm and moderate to dry lowland climate (from the west to east part of the region, respectively) with an average yearly temperature 11.4℃, and average yearly rainfall of 699 mm having the highest spring rainfall regime in June. The experiment was laid out in randomized block design with four replications and comprised of untreated control and three different weed management strategies: chemical control, mechanical control, and combination of chemical and mechanical treatments (Table 1).
All the plots have an area of 300 m². Garlic cloves were planted on October 25th, 2018 at a rate of 2.800 kg/ha⁻¹ after seedbed preparation in first decade of October. The previous crop was sweet corn. Before the garlic was planted, the soil was thoroughly ploughed, leveled and fertilized with recommended doses of NPK (Parađiković, 2009). Row to row and plant to plant distances were kept 30 cm and 10 cm respectively. On plots with chemical treatments pendimethalin at a dose of 2,5 l/ha⁻¹ was sprayed 4 days after planting (DAP) and before the garlic emergence, while combination of clopyralid and fluroxypyr (0,75 + 0,75 l/ha⁻¹) was applied post emergence in 180 DAP, when
garlic has developed 3-4 leaves. Mechanical weed control included three hand weeding during the crop season (in early, mid and late of spring 2019). Combination of chemical and mechanical weed control included PRE-EM (pendimethalin) and POST-EM application (clopyralid and fluroxypyr) of herbicides on the same dose and time as on plots with chemical treatments and one mechanical weeding in the beginning of June 2019. No weeding was done in the weeded control plots. Garlic was harvested by hand on 7th July 2019 using a small hand-hoe.
Source: Author’s research object
*PRE-EM: pre emergence application of herbicide; POST-EM: post emergence application of herbicide; DAP: days after planting
Data were collected at the end of the growing season (during the harvest) after the effect of herbicides and mechanical cultivation had become evident. Remaining weed community was sampled by means of four randomly placed 1 × 1m quadrates in each plot. Weeds were cut at ground level, separated by species, counted and weight. Bulb yield from these quadrats were also recorded (in kg/m⁻²), and then converted to tons per ha for the economic analysis. Prior to statistical analyses the data were checked for normal distribution and homogeny of variance, and then were subjected to ANOVA using PROC GLM procedure in SAS (SAS v9.4, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC). The means were compared with Fisher’s Protected LSD test at the 5% level of probability. To determine the most economically acceptable treatment, a partial budget analysis was performed to estimate the gross value of the garlic bulb yield from different weed management methods. The cost of production and gross margin of each treatment was calculated considering the current rate of agricultural operations right from preparatory tillage to harvesting including cleaning as well as market prices of inputs, seeds, fertilizers, insecticides and other variable costs.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3. 1 Weed infestation
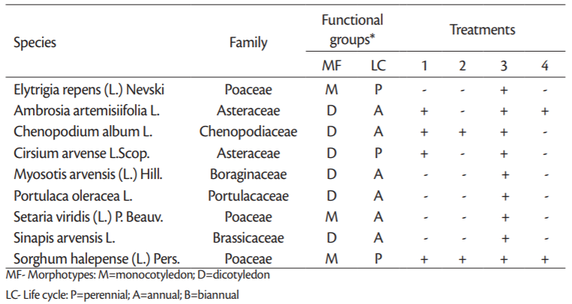
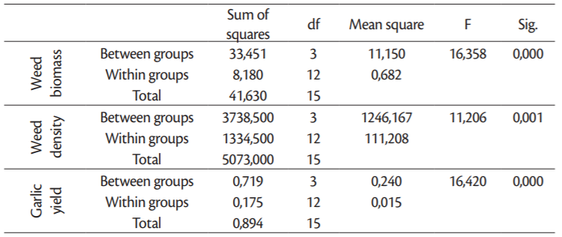
The naturally occurring weed community found in the study area consisted of a mix of annual and perennial grasses and broadleaf weeds, common to this region (Štefanić et al., 2017). Weed community was dominated by a few species that had high relative abundance values and density (Table 2), while most of the species were of low abundance and density per square meter and with the low impact on the crop.
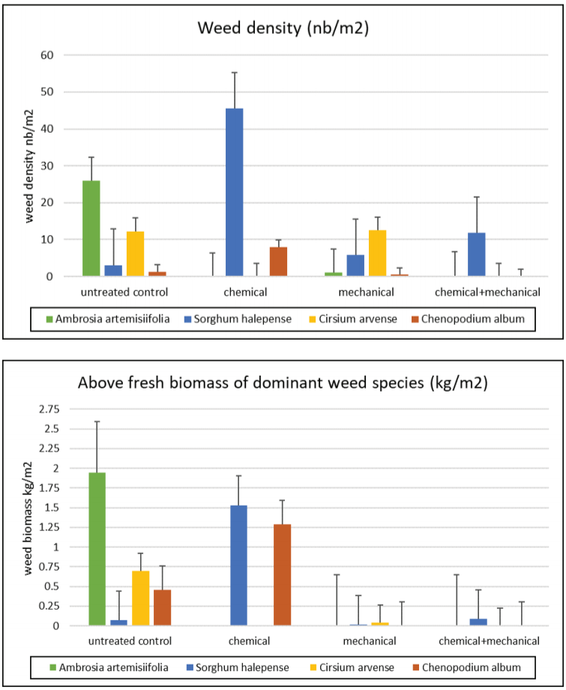
The mayor weeds found in the experimental plots were: Sorghum halepense (Johnsongrass), Ambrosia artemisiifolia (common ragweed), Cirsium arvense (Canada thistle) and Chenopodium album (lambsquarters). Among them S. halepense and A. artemisiifolia are not only noxious weeds in the fields, but also a serious plant invaders in agricultural landscapes of the investigated region as well as in many parts of Europe (Chapman et al., 2017,Stefanic et al., 2017b). Dicot weeds were dominating more in the field than monocots, as well as annuals in relation to perennials. Weed control methods significantly affected the weed biomass and weed density (Table 3,Figure 1). Common ragweed (A. artemisiifolia) developed the significant aboveground biomass (1,95 kg/m²) and had the highest density (26 plants) per m² on untreated control plots, followed by C. arvense and C. album. Weed control efficiency ranged from 96% and 91% (chemical + mechanical and mechanical control respectively) to only 12% (chemical treatment). Mechanical and combination of chemical and mechanical treatments successfully controlled weeds, having only few shoots of dominant weeds per m² with insignificant biomass.
Source: Author’s original work
Application of herbicides lead to insufficient control efficacy of two noxious weed species S. halepense and C. album, although in some other studies pendimethalin and clopyralid demonstrated a satisfactory control, particularly for Chenopodium album (Ujgur et al., 2010.,Sahoo et al., 2018). These weeds developed at the end of growing season in average 1,53 kg and 1,29 kg of fresh above biomass per 1 m² respectively. Regarding plant density per m², S. halepense had 45, and C. album 8 shoots in average.
Source: Author’s original work
Results of this study are in agreement with experiment done byVora and Mehta (1998) where herbicide application alone did not control weeds effectively but herbicide application followed by one hand hoeing gave the best results in garlic crop. Therefore, in minor crops like garlic, low availability of herbicides imposes to adopt an integrated use of non-chemical weed control method, or to combine those methods with existing herbicides option (Rahman et al., 2011). Also, the superiority of the mechanical and combination of chemical and mechanical weed control could be explained on the basis of better growth and higher uptake of nutrients under these practices which are corroborated with the findingsMalik et al. (2017) andVermani et al. (2001.). Mechanical control methods, however, over the last 20 years have become effective, fast and do not leave chemical residues on crops (Pannaci & Tei, 2014).
3. 2 Garlic yield
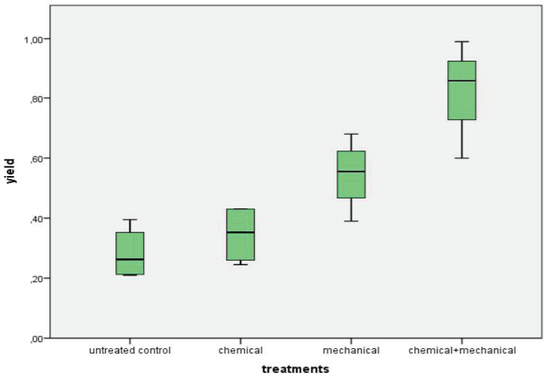
Weeds can reduce garlic yields considerably if not managed properly (Table 3,Fig. 2). This results, in which weeded check caused 82% reduction in the garlic yields when compared with chemical and mechanical treatment, show that weed control is very important for garlic production. However, in some other studies, due to unrestricted weed growth, yield loss in garlic was even up to 94.8% due to weed competition (Anon, 2009). The highest yield (8,3 t/ha) was obtained with combination of chemical and mechanical weed control. Mechanical weed control throughout the growing season gave the significantly lower yield (5,5 t/ha), while chemical application and weeded check had the worst results with 3,5 t/ha and 2,8 t/ha, respectively. Also, these bulbs were of low quality and not for commercial sale.
3. 3 Economic analysis
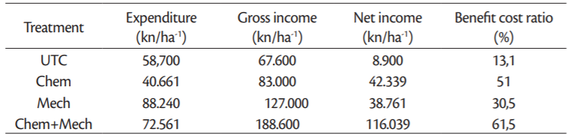
Weed management is an important factor that influences the economic importance of garlic production. Weeds not only compete for nutrients, water, light, space but also increase cost of labor and render the harvesting operations difficult. The impact of weed management method on expenditure, gross income, net income and benefit: cost ratio is shown inTable 4.
Source: Author’s original work
Based on a current market prices of herbicides, cultivations, and the wholesale price of garlic it could be concluded that combination of chemical and mechanical control method gave the best benefit cost ratio. Mechanical cultivation, due to the high labor costs, did obtained satisfactory economic benefit. Therefore, an integrated weed management approach (IWM) could be a good option for a successful garlic production. IWM provides diverse weed control tools that are feasible in a given socio-economic situation (Mehmood et al., 2006,Lamichhane et al., 2017).
4. CONCLUSION
In present study, weed community in garlic dominated with johnsongrass (Sorghum halepense), common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia) Canada thistle (Cirsium arvense) and lambsquarters (Chenopodium album). Those weeds compete with garlic for nutrients, soil moisture, space, and light and considerably reduce the yield, quality and value of the crop through increased production and harvesting costs. Chemical treatment alone did not provide a season long weed control. Manual weeding is a very expensive laborious method of weed control, even often damages the crop. This research demonstrated that good option (higher yield and economic benefit) could be implementation of IWM i.e. combination chemical and mechanical weed control. This treatment successfully controlled weeds, gave the highest yield and the best economic benefit.