1 Introduction
Tourism is a multifaceted concept (Parfinenko et al., 2019; Prokopenko et al., 2019). Even if we consider the sector of international marine tourism, a wide range of issues and approaches that determine its prospects and trends can be observed in the scientific literature. Marine tourism includes numerous services, such as marine tourism companies, cruise companies, charters, ports, the underwater tourism industry, shore service, etc. Furthermore, the role of governance at all levels, including schemes, laws, guidelines and concepts, public leaders and the scientific community, cannot be underestimated in the development of international marine tourism. Tourists themselves, the population of tourist regions and their level of social and economic development also play an essential role in tourism development. In addition, tourism is closely related to the natural environment of seas and oceans, as well as coastal areas, because the purpose of most tourist trips for recreation is close contact with nature.
Sustainable development is a fundamental principle of developing countries as a whole, as well as industries and territories (Shvets et al., 2023; Prokopenko et al., 2021; Prokopenko & Miśkiewicz, 2020). Sustainable development as a socio-ecological-economic development priority is associated with the Scheme for international cooperation, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) (United Nations, 2015). The concept of sustainable tourism is fully included in the Global Code of Ethics in Tourism, the implementation of which among its member countries is organized by the World Tourism Organization (UNETO).
Bibliographic studies of scientific publications devoted to marine tourism have recently been carried out by numerous authors. In order to determine the state and trends of the coastal and marine tourism (CMT) industry, a study by Duan et al. (2022) was devoted. The researchers conducted a qualitative bibliographic analysis of publications for the years 1990-2020, taking into account such variables as: Productive Countries, Organizations, Authors, Subject Categories and Main Source Journals and Keywords. Connections between them were also established. As a result, the main research topics were identified, namely: (1) the sustainable development of CMT, (2) the impact of CMT on destinations, (3) CMT management and conservation, and (4) the impact of climate change on CMT.
Selvaduray et al. (2022), based on bibliometric analysis, identified the main clusters of problems that the maritime tourism industry suffers from. They were (a) governmental and political support, (b) environmental issues, (c) cooperation among stakeholders, (d) maritime tourism law and policies, (e) technological matters, and (f) maritime tourism knowledge. This study proposes a smart maritime tourism market, the study defines Smart Maritime Tourism (SMT) as a new type of maritime tourism that employs Virtual Reality (VR) to encompass and change the foreland, seaport, and hinterland segments of the industry (Selvaduray et al., 2022).
The study focused on the conceptual apparatus was carried out by Martinez Vazquez et al. (2021). The authors followed the evolution in the Number of Publications per year in relation to the terms “nautical tourism”, “maritime tourism” and “marine tourism”. They identified the most cited articles, productive authors, affiliations, countries, regions, and relationships. In our opinion, the main result of this study is the categorization of the concepts of "nautical tourism", "maritime tourism" and "marine tourism" and the identification of the need to define a new concept of "blue tourism". A new concept was proposed that integrates the subsector of the blue economy and the blue growth strategy, under the name of “blue tourism”, with the sea as the protagonist and all those tourist activities of leisure and recreation developed in this environment.
There are studies of trends in eco-tourism and sustainable tourism (Shasha et al., 2020; Mauleon-Mendez et al., 2018; Garrigos-Simon et al., 2018, etc.), but they do not touch on the topic of coastal and marine tourism. The development of marine tourism in combination with the socio-ecological and economic development of territories and countries as a whole in order to maximize the socio-ecological and economic benefits of tourism and minimize its negative impact on nature and society is a priority of many scientific studies.
Our research aims to determine the trends of international marine tourism in the context of sustainable development priorities with the help of bibliographic and contextual analysis of scientific literature. Also, the goal is to present possible prospects for developing international marine tourism based on the conclusions and recommendations of selected scientific publications.
2 Methodology
The research methodology consists of bibliographic and content analysis of relevant scientific publications investigating international marine tourism aimed at sustainable development. We used the Dimensions research information database search engine for bibliographic search and analysis. The database searches among Publications, Grants, Patents, Clinical Trials, Policy Documents, and Records with Altmetric attention. A total of 153 million research records were searched [Bode, 2019].
A wide variety of terms refer to marine tourism and sports, recreational activities at sea and in other aquatic environments, international sea voyages, walks and trips along coastal waters and other activities that can be attributed to marine and coastal tourism. Definitions of the most used terms such as “nautical”, “maritime” or “marine” tourism often overlap each other's spheres of definition. A rather detailed study of the categorizations of these and other terms was conducted by the authors Martinez Vazquez et al. (2021). Since for the purposes of this study, it is not important enough to clearly establish the difference between the definitions, we will use the term "marine tourism" for the search and analysis, and have in mind a very broad concept, based on the category "blue tourism" (Martinez Vazquez et al., 2021) with the sea as the protagonist and all those tourist activities of leisure and recreation developed in this environment.
Search using Dimensions on the intersection of two key phrases in the title and/or abstract of the article "marine tourism" and "sustainable development" results in 949 publications. The search was carried out on the request "marine tourism and sustainable" since it includes unfinished phrases such as "sustainable development", "sustainable economy", "sustainable tourism", etc. Publications from 1973 to 2022 are included in the search. The found publications consist of 750 Articles, 133 Chapters, 31 Preprint, 15 Edited Books, 12 Proceedings and 1 Monograph [Search, 2022]. Additionally, Datasets from 1,424 sources, Patent 1 and Policy Documents 295,882 are available for analysis upon request.
3 Results
Each publication belongs to a particular group of research categories. According to Fields of Research (ANZSRC 2020), dimensions implement automatic machine-based division into research categories. The Fields of Research (FoR) classification is a component of the 2020 Australian and New Zealand Standard Research Classification (ANZSRC) system. Each publication can be assigned to several research categories. Table 1 presents the results of the division of publications for a given search into groups of research categories according to Fields of Research (ANZSRC 2020). Most of the research belongs to the research category 41 Environmental Sciences (438 publications). The following categories have the most excellent results: 35 Commerce, Management, Tourism and Services, 37 Earth Sciences, 48 Law and Legal Studies, 31 Biological Sciences, 40 Engineering and 44 Human Society.
Table 1 The division of publications for a given search into groups of research categories according to Fields of Research (ANZSRC 2020).
Source: Authors.
Publications on topics at the intersection of marine tourism and sustainable development began to be published in 1987 (one publication). After that, for a long time, there were few publications on the intersection of the selected topics (one in 1989, two in 1993, one in 1995, two in 1996, two in 1997, and one in 1998) until 1999, when the trend of increasing interest in the given topic began. Since then, the most significant number of such studies was conducted in 2020 – 180 publications. Figure 1 shows the number of publications published each year. Here Publications is the number of publications related to the search. The analytical view shows the total number of related publications. The values per year are the years in which the publications were published.
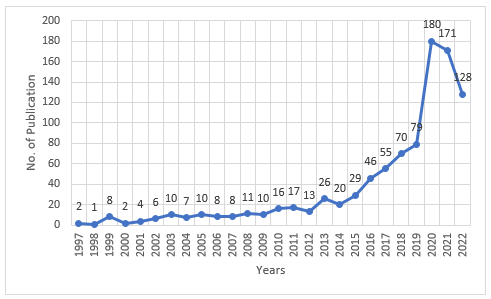
Figure 1 The number of publications according to the search published in each year. Source: Authors.
With the help of the Dimensions service, we analyzed the selected publications according to the search, as well as according to the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Publications are divided according to the SDGs with which the publication is more closely related, thus covering research areas aligned with the objectives. According to the selected search, the publications were divided into the publications were distributed among all 17 categories according to the Sustainable Development Goals. The most significant number of publications belongs to the following: 14 Life Below Water, 15 Life on Land,13 Climate Action,8 Decent Work and Economic Growth,11 Sustainable Cities and Communities,7 Affordable and Clean Energy and12 Responsible Consumption and Production. Figure 2 shows the number of publications in each research category (related to our search, here is Sustainable Development Goals).
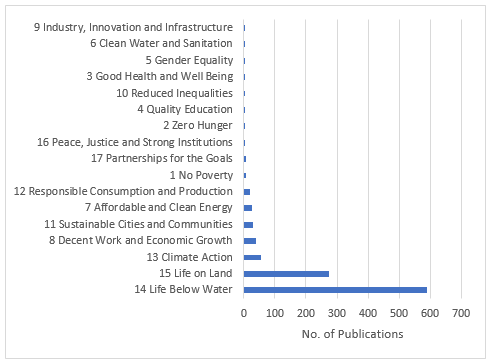
Figure 2 The number of publications in each research category according to the search. Source: Authors.
The publications highlighted in the research are published from different sources. A total of 949 publications were published in more than 180 printed sources. The majority of them, in particular 67 publications, belong to the authors in the Journal of Coastal Research (Journal, 2022). Table 2 shows the number of publications by Source Titles. The table presents only journals where ten or more articles were published according to our search. Publication citations are the number of times other publications in the database have cited a publication. The analytical view provides the following options to aggregate citations: total (the total number of citations in the database of relevant articles) and means (the average value of citations for each article from the search in the corresponding printed edition).
Table 2 The number of publications by Source Titles.
| № | Source Title | Publications | Citations, total | Citations, mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Journal of Coastal Research | 67 | 161 | 2,40 |
| 2 | Ocean & Coastal Management | 41 | 1,776 | 43,32 |
| 3 | Marine Policy | 38 | 675 | 17,76 |
| 4 | IOP Conference Series Earth and Environment | 31 | 21 | 0,68 |
| 5 | Sustainability | 17 | 162 | 9,53 |
| 6 | Tourism in Marine Environments | 16 | 210 | 13,13 |
| 7 | Frontiers in Marine Science | 12 | 97 | 8,08 |
| 8 | Journal of Sustainable Tourism | 11 | 391 | 35,55 |
| 9 | Environment, Development and Sustainability | 10 | 212 | 21,20 |
Source: Authors.
The network of researchers related to our search is presented in Figure 3. The relatedness of researchers is determined based on their number of co-authored publications. As you can see, the network of researchers is a rather extensive and not interconnected network of scientists, except for one largest group. Figure 3 shows the network of the first 100 researchers ranked by the number of publications on this topic, publications with more than 25 authors are also ignored.
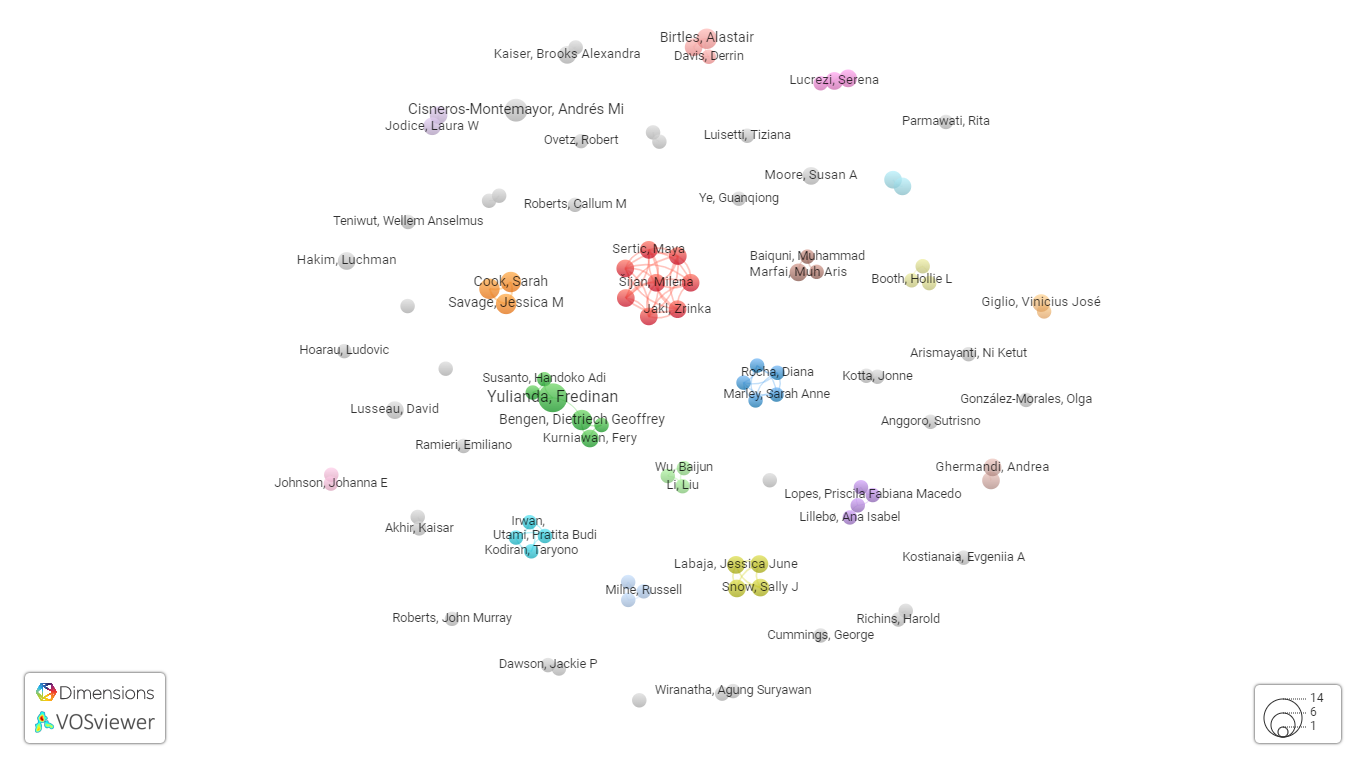
Figure 3 The network of researchers. Source: Authors.
Figure 4 shows only the most extensive set of related items (among the network of researchers from Figure 3).
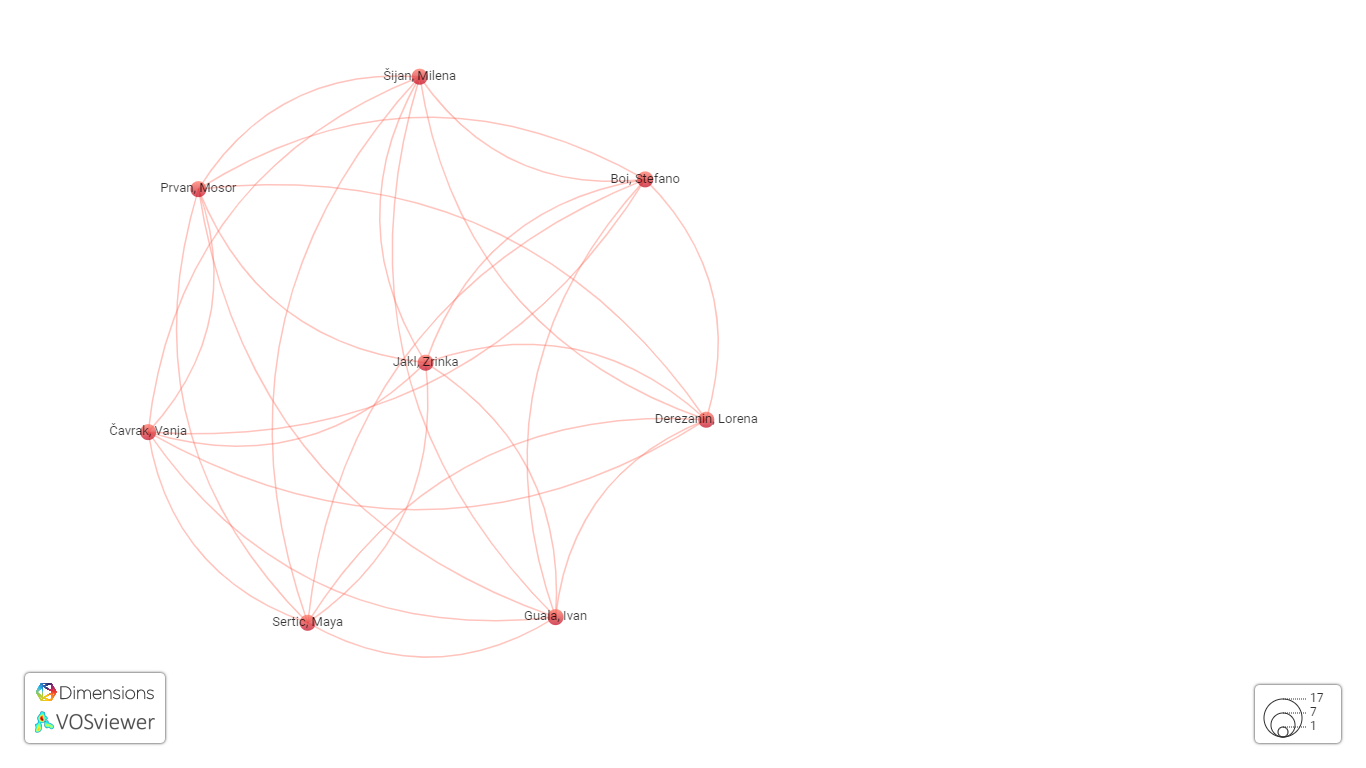
Figure 4 The network of researchers (the most extensive set of connected items). Source: Authors.
Table 3 presents the results of the analysis of scientific publications devoted to the development of marine tourism and the promotion of the concept of sustainable development. The analysis of the mentioned articles was carried out from the point of view of the development prospects of international marine tourism with the application and dissemination of the concept of sustainable development. Articles for analysis in this study were selected randomly, taking into account the citation index from the list of articles selected in the database using the Dimensions service. A total of 7 articles were analyzed and summarized in a table that includes the author and the year of publication of the study, sustainability concerning the development of marine tourism, methodology, and prospects for the development of international marine tourism (conclusions and recommendations).
Table 3 Prospects for the development of international marine tourism with the application and dissemination of the concept of sustainable development
| № | Authors (year) | Sustainability concerning the development of marine tourism | Methodology | Prospects for the development of international marine tourism (conclusions and recommendations) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nguyen Xuan Dien et al. (2019) | The situation in each of the components of sustainable development in coastal areas is described: economic (GDP), social (education, access to resources, poverty), and environmental (territory pollution, erosion, garbage, etc.). | Descriptive statistics methods. Data resources are based on analytical data from the General Department of Statistics and the General Department of Tourism of Vietnam from 2005-2015. |
Recommendations are offered for (1) the Ministry of Culture, Sport, and Tourism of Vietnam: development of a sustainable strategy; organization of scientific research related to the sustainable development of marine tourism; and direct exploitation of marine tourism resources at the macro level. (2) the Coastal Localities: a plan to concentrate on the human resource; promoting administrative reform, and promulgating many investment incentives and preferences; strengthening the activities of tourism business divisions; raising awareness of businesses, local communities and tourists about the problem of protecting the marine and coastal environment. |
| 2 | Islahuddin at al. (2021) |
Achieving sustainable coastal area development uses integrated management of coastal and marine areas. Sustainable tourism is considered a perspective, a top-priority direction of development. | Analysis and explanation of the model the reconstruction of the actor collaboration model in the development of marine tourism destinations. Data and information were obtained using observation, interviews, Focus Group Discussion, and documentation. | The results show that there is a reconstruction of a descriptive model of actor collaboration in developing marine tourism destinations based on a knowledge creation model that includes four dimensions. Community-Based Tourism (CBT) characterizes the concept of developing tourist destinations through the socialization (S) of local community empowerment programs that emphasize externalization (E) or empowerment of specific communities better to understand the values and assets of marine tourism |
| 3 | Karani et al. (2020) | Sustainable development in terms of the growth of the blue economy, namely its parts specific to the African region, including the development of tourism | Desk-top literature review and secondary data source on LMEs in Africa for the blue economy, professional experts' views and opinions, and additional data gathered from field visits to 13 African countries | It is expected that the development of the Blue Economy, coastal and marine tourism, climate resilience, the development of eco-services, etc., will lead to the sustainable development of the African region |
| 4 |
Henderson, J. (2019) | Promoting sustainable development through greater attention to maritime cultural heritage (MCH), including maritime tourism. Tourism is considered a link between cultural heritage and economic development. | Qualitative methods of analysis | It is concluded that the presence of MCH should be considered crucial for evidence-based decision-making in the coastal and marine sectors. Approaches based on MCH must be included in projects aimed at the sustainability of seas and coastal areas. |
| 5 | González-Morales at al. (2021) | The study analyzes the corporate social responsibility of marine tourism companies as a set of specific voluntary strategic actions that contribute to sustainable development | Quantitative methods are statistical methods for evaluating the results of questionnaires, namely binary logistic regression analysis. Qualitative methods - case study and analysis | A conclusion is made about marine tourism companies' general social and environmental responsibility. Sectors are highlighted that are more or less regulated and, accordingly, are subject to changes in social responsibility in different ways. |
| 6 |
Löhr et al. (2017) | Sustainable development in the context of the impact on it of the pollution of the sea by microplastics | This paper reflects on the sources and effects of marine litter and the effects of policies and other actions taken worldwide. |
The search for appropriate responses could be based on possible interventions and a profound understanding of the context-specific factors for success. However, the effects of policies and other initiatives still need to be improved. Moreover, all initiatives' scope, timeframe and dynamics are distinctly different, and orchestration at all levels, in close cooperation, is currently lacking. Successful solutions to the marine litter problem require coordinated action amongst many public and private actors. Successful actions aim at a diversity of goals, ranging from changing consumer behaviour, introducing new technologies, designing, implementing and enforcing a multitude of plans, policies and laws to full-scale revision of current waste production, use and management practices. s, and from the local to the global level |
| 7 |
Narendra N. Dalei at al. (2021) | Sustainable ocean tourism is seen as necessary to balance the ecological, economic, social and cultural aspects of the development of ocean tourism. | A primary online survey of international tourism experts' perceptions using Google Forms. A regression model was used to analyze the results of 30 valid answers. |
Although India's foreign country legislation significantly improves the sustainability of ocean tourism, India's foreign policy and government institutions still need to be more significant in predicting the sustainability of international maritime tourism. Suggested changes in the management policy of India |
Source: Authors.
The importance of considering sustainable development as a concept that must be observed to some extent in the prospects of the development of marine tourism is undeniable in all studies. Since the tourism sector includes many industries and concerns many aspects, there is a diversity of approaches to researching the prospects of international marine tourism.
Henderson (2019) refers to sustainable development through greater attention to marine cultural heritage (MCH), including marine tourism. Tourism is seen as a link between cultural heritage and economic development as part of sustainable development (Henderson, 2019).
Nguyen Xuan Dien et al. (2019) refer to the analysis of the situation for each of the components of sustainable development of coastal areas: economic (GDP), social (education, access to resources, poverty), environmental (territory pollution, erosion, garbage, etc.) (Nguyen Xuan Dien, 2019).
Approaches of management concepts to the integrated management of coastal and marine territories in order to achieve sustainable development of coastal territories are used by Islahuddin et al. (2021). They consider sustainable tourism a promising and a priority development direction (Islahuddin, 2021).
The growth of the blue economy as one of the concepts associated with sustainable development, particularly its parts, characteristic of the African region, including the development of tourism, is addressed by Karani et al. (2020).
A study by González-Morales et al. (2021) analyzed the corporate social responsibility of marine tourism companies as a set of specific voluntary strategic actions that contribute to sustainable development. With the help of quantitative statistical analysis methods and the use of cases, maritime tourism companies general social and environmental responsibility was investigated. As a result, the management sectors of marine tourism companies are highlighted, which are more or less regulated and, accordingly, are subject to changes in social responsibility, including in the direction of sustainable development, and vice versa, have an established implementation practice and do not perceive changes.
Sustainable development in the context of the impact on it of the pollution of the sea with microplastics is studied by Löhr et al. (2017). This paper examines the sources and impacts of marine litter and the implications of policies and other actions taken worldwide. However, it is concluded that the results of the policy and other initiatives are still largely insufficient. It is concluded that only interventions in deeply researched specific success factors can lead to relevant responses. In addition, the problems of management and lack of coordination at all levels, according to the authors' results, as well as in the studies of Islahuddin et al. (2021) and Dalei et al. (2021), are proposed to solve.
The concept of sustainable ocean tourism is necessary to balance the environmental, economic, social and cultural aspects of ocean tourism development in a study by Dalei et al. (2021). Based on the regression analysis of the results of the primary expert survey, the authors propose changes in the management policy of India. Under their guidance, management policies need to be reviewed and reformulated to make changes essential drivers for the sustainability of international marine tourism.
4 Conclusion
Taking into account the wide variety of components of international marine tourism and the indisputable importance of increasing the socio-ecological and economic results of tourism, as well as the prevailing trend in minimizing the negative environmental impact of tourism on the natural environment, broad prospects for the development of tourism are opening up.
The content analysis of the selected publications makes it possible to talk about the need for management reforms at all levels through the concept of sustainable development and the Global Code of Ethics in Tourism. This goal requires the adoption by even more world countries of the philosophy of the Global Code of Ethics in Tourism and approximation to its standards. Moreover, it is also necessary to implement the mentioned concept in its political and economic strategies in the middle of the country at all levels of tourism development.
According to the results of the bibliographic analysis, it was evident that the development of scientific research aimed at implementing the concept of sustainable marine tourism and the Global Code of Ethics in Tourism needs attention.
The next problem is the clustering and externalization of marine tourism according to the orientation toward a particular community. Since the negative socio-ecological-economic consequences of tourism are borne by the territory and society of a specific local community, large-scale tourism, which is international marine tourism, is accumulated internationally.
Furthermore, finally, the blue economy and the protection of natural resources of coastal areas as a basis for implementing marine tourism activities need further development.
The results of this study can be helpful both to the scientific community and the general public, as well as to specialists in the field of bibliography.
Funding: The research presented in the manuscript did not receive external funding.
Author Contributions: Data Collection, Data curation, Research, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing, Review, and Editing; all authors contributed equally.
