INTRODUCTION
Prostate cancer (PCa) is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death among men worldwide (1). Each year, an average of 750,000 men are diagnosed with prostate cancer and 10 % of prostate cancer patients die. Although the incidence of this male-only cancer is high, it constitutes 6 % of all cancer-related deaths (2). Despite significant advances in treatment modalities, novel therapeutic approaches remain essential to improve patient outcomes. Tannic acid, a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound in various plant sources, has drawn more attention due to its potential anticancer properties (3). According to studies, liver, breast, and prostate cancer cells cause regulation in signal transduction mechanisms and apoptosis pathways (4–8). Tannic acid was found to increase DNA binding activity in the P38/STAT1 pathway by increasing ser727 phosphorylation. Tannic acid also inhibits STAT1 and STAT3 when it binds to EGFR. Tannic acid treatment of T cells was discovered to inhibit the proteasome substrate, which results in the cell being dragged to death at the G1 control point of the cell cycle (9). Previous studies have demonstrated that tannic acid exerts selective cytotoxic effects on cancer cells including lung cancer (10), breast cancer (11), and liver cancer (12), all while protecting healthy cells. However, the precise molecular mechanisms behind these effects are still unknown, particularly in the context of prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is frequently initiated by loss-of-function mutations in genes that play crucial roles in tumor suppression and the apoptotic pathway (13). Apoptosis, a tightly regulated process of programmed cell death, plays a critical role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and suppressing tumor growth (14). Dysregulation of apoptotic pathways is often associated with cancer progression and resistance to therapy (15). Epidemiological studies have revealed elevated expression levels of the anti-apoptotic BCL2 gene in PCa, suggesting a significant association between BCL2 expression and PCa development (16). Moreover, the presence of other anti-apoptotic factors, such as survival, has been linked to an increased risk of PCa progression (17).
Understanding the complex interaction of apoptotic regulatory pathways and their role in PCa pathogenesis is essential for developing targeted therapeutic strategies. To provide light on new therapeutic targets for treating this challenging malignancy, our study attempts to clarify the effect of tannic acid on apoptotic gene dysregulation in PCa. By examining the expression profiles of key apoptotic regulators in response to tannic acid treatment, this study contributes to the growing body of knowledge regarding PCa biology and may pave the way for the development of more effective treatment modalities. The findings have promising implications for the use of tannic acid as a novel approach in PCa therapy, enhancing our understanding of its mechanisms of action and potential benefits in precision oncology.
EXPERIMENTAL
Chemicals
Tannic acid (TA; T0200) was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (USA). PNT1A, PC-3, and LnCap cell lines, F-12K and RPMI-1640 mediums, FBS, and penicillin/streptomycin were purchased from ATCC (American Type Culture Collection, USA). Alamar Blue and TRIzol reagents were obtained from Invitrogen Life Technologies (USA). iScript cDNA synthesis kit and SYBR Green were purchased from Bio-Rad Laboratories (USA). All purchased chemicals and solvents were of the analytical standard at the highest grade of purity available.
In vitro cytotoxicity studies
Cell culture. – PNT1A (RRID: CVCL_2163) (prostate control), PC-3 (RRID: CVCL_0035) (androgen-independent) and LnCaP (RRID: CVCL_0395) (androgen-dependent) human prostate adenocarcinoma cells were cultured in F-12K medium for PC3 cells and RPMI-1640 medium for PNT1A and LnCaP cells supplemented with 10 % FBS and 1 % penicillin/streptomycin. The cells were incubated at 37 °C and 5 % CO2 in an incubator (BINDER, USA).
Cell viability and proliferation studies. – The cells were divided into two groups: untreated (NT) and tannic acid-treated and then incubated for 48 hours. To assess cell proliferation and cytotoxicity, an Alamar Blue assay was employed (Invitrogen, Thermo Fischer Scientific, USA). 3 × 104 of PNT1A, PC-3, and LnCaP cells were seeded into 24-well plates and treated with varying concentrations of tannic acid (0–200 µmol L–1) for 48 hours. Cells treated with Alamar Blue (10 % of the well volume) were incubated at 37 °C for 3 hours. Alteration in color was determined using a fluorescence spectrophotometer (BioTech Synergy HTX Multimode Reader) with 560/590 nm (excitation/emission) filter settings. IC50 values were calculated using GraphPad Prism 8 ( GraphPad Software, Inc., Version 8.4.3., USA) based on a sigmoidal plot of the logarithm of tannic acid concentration against the percentage of cell growth inhibition. Results were presented as a percentage of cell viability (%) compared to the NT group.
Investigating the impact of tannic acid on apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines. – To evaluate the effects of tannic acid on the cell death mechanism, flow cytometric analysis was performed using a flow cytometer (BD FACSCalibur, USA) equipped with appropriate filters for detecting Annexin V-APC and 7-AAD fluorescence. A minimum of 10,000 events were acquired for each sample. Compensation controls and unstained cells were used to set up the flow cytometer. Data analysis was performed using flow cytometry software FlowJo™ v10.8 Software (BD Life Sciences, USA). Flow cytometry data allowed the discrimination of different cell populations based on their Annexin V-APC and 7-AAD staining patterns. The following cell populations were identified: viable cells (Annexin V-APC and 7-AAD negative), early apoptotic cells (Annexin V-APC positive and 7-AAD negative), late apoptotic/necrotic cells (Annexin V-APC and 7-AAD positive), and necrotic cells (Annexin V-APC negative and 7-AAD positive).
Determination of the impact of tannic acid on apoptosis pathway genes in prostate cancer cell lines
Total RNA from PNT1A, PC-3, and LnCaP cell lines was isolated using the TRIzol method (18). Cells cultured in 24-well plates were treated with TRIzol and incubated briefly before transferring the lysates to Eppendorf tubes. After centrifugation, the RNA-containing aqueous phase was collected, and isopropanol was added for RNA precipitation. The RNA pellet was washed, air-dried, and reconstituted in ddH2O. RNA quality was evaluated using Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Inc., Germany) ensuring samples with distinct 18S and 28S peaks, A260/A280 ratio (1.8–2.0), A260/A230 ratio (≥ 1.8), and RIN value (≥ 7). Suitable RNA samples were stored at –80 °C for future studies. The iScript cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA) was used to synthesize the cDNAs from total RNAs by Thermal cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA). 20 µL of total reaction mixture contains 2 μg total RNA, 4 µL 5X iScript reaction mixture, 1 µL iScript Reverse Transcriptase, and RNase-free water. After incubation at 25 ºC for 5 minutes, reverse transcription was started at 46 °C and incubated for 20 min. 25 µL of qRT-PCR reaction mixture contains 12.5 µL of SYBR Green, 2 µL of cDNA, and 1.25 µL of reverse and forward primers. RT inactivation was performed at 95 °C for 1 min. The qRT-PCR cycling conditions included an initial denaturation of 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s and annealing of 60 ºC for 30 s using CFX Connect Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA).
To assess the effects of tannic acid on the apoptosis pathway in prostate cancer cells, we utilized apoptosis panels (Qiagen, 330231_RT² Profiler PCR Array). This comprehensive panel consists of 84 genes associated with apoptosis, enabling a thorough examination of gene expression changes. The relative mRNA expression was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method (19). GAPDH, GUSB, PPIA, B2M, HPRT1, PGK1, ACTB, and RPL13A were used as an internal standard.
Statistical analysis
One-way ANOVA, along with a post-hoc analysis of Tukey's Honestly Significant Difference (HSD), were performed to determine the gene-level expression alterations between the experimental groups. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Subsequently, statistical reliability values ( p < 0.05) and fold change were calculated for each gene on the array. The results were further refined through filtering based on mean p-value and fold change by ranking from high to low. The mRNA expressions altered more than 2-fold were accepted as statistically significant. All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS software (IBM Corporation, USA, Version 23.0).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Cytotoxic potential of tannic acid on human prostate cell lines; PC-3 and LnCaP were analyzed. According to the results, the IC50 value in LnCap and PC-3 prostate cancer cells was found to be 29.1 and 35.3 µmol L–1, respectively, while the IC50 value in PNT1A, which were used as prostate control cells, was higher than 200 µmol L–1 (Fig. 1a). It was evident that with the treatment of tannic acid, the percentage of total apoptotic cells, shown in red color in Fig. 1: b-2, has increased as compared to the untreated group (Fig. 1: b-1). Particularly, early-stage apoptosis (Annexin V-FITC+/7-AAD−) ratios were markedly increased (Fig. 1: c-2, d-2) in tannic acid-treated PC-3 and LnCaP cells as compared to the untreated cells (Fig. 1: c-1, d-1), respectively.
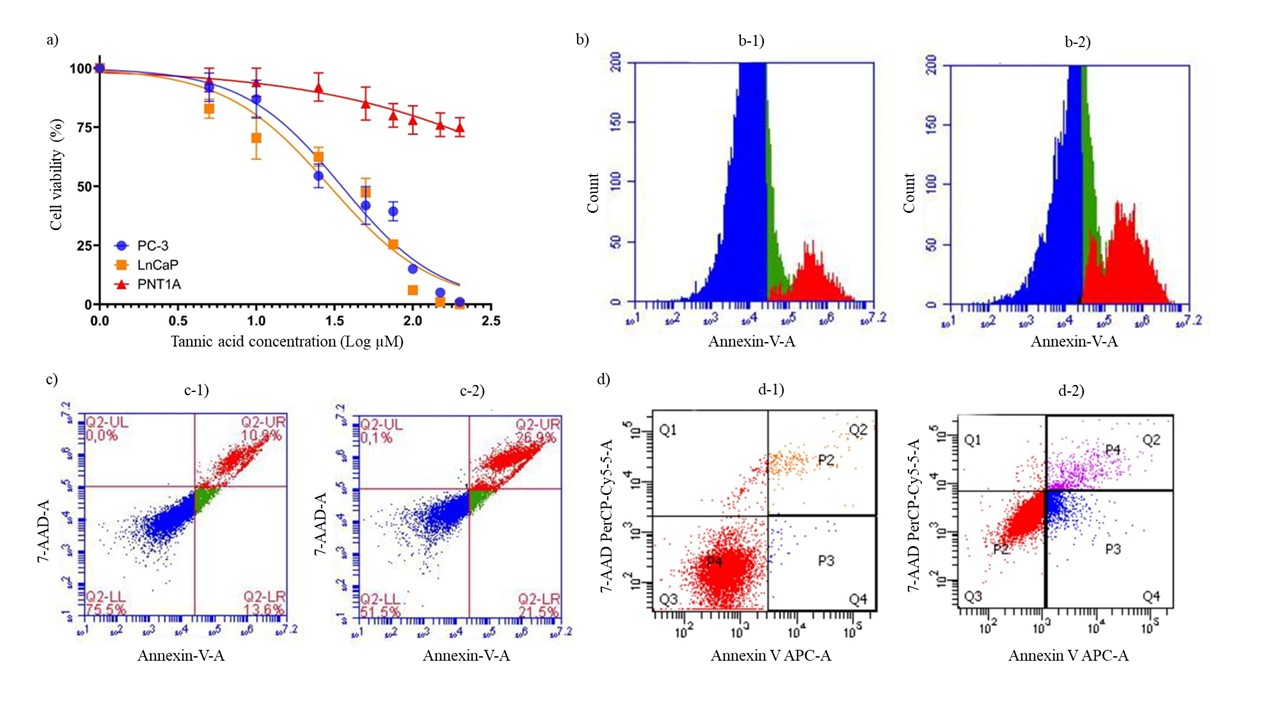
Fig. 1. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis analysis of PC-3, LnCaP, and PNT1A cells following tannic acid treatment. a) Cell viability was measured using Alamar blue method after treatment with tannic acid; b-1) histogram of Annexin V/7 AAD staining of non-treated cells, b-2) Histogram of Annexin V/7 AAD staining of tannic acid-treated cells, c) Scatter plot of Annexin V staining vs 7AAD staining, Quadrants show upper left (necrotic cells), upper right (late apoptotic cells), lower left (live cells), and lower right (early apoptotic cells); c-1) scatter plots of non-treated PC-3 cells, while c-2) shows tannic acid treated PC-3 cells; d) scatter plots of Annexin V-APC vs 7-AAD staining, Quadrant charts show; Q1: necrotic cells (Annexin –, 7-AAD +); Q2: late apoptotic cells (Annexin +, 7-AAD +); Q3: viable cells (Annexin –, 7-AAD –); Q4: early apoptotic cells (Annexin +, 7-AAD –); d-1) scatter plots of non-treated LnCaP cells, and d-2) Scatter plots of tannic acid treated LnCaP cells.
D own-regulatedThe mRNA expression levels of apoptotic genes in PC-3 and LnCaP cells treated with tannic acid were analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR. The relative normalized expression of each gene was compared to the regulation threshold to determine whether the genes were up-regulated or down-regulated upon tannic acid treatment. Genes that change 2- fold or more after treatment with tannic acid are up- and down-regulated genes that show statistically significant change, whereas those that are 2-fold or less are expressed with black dots and represent genes that do not show a statistically significant change (Fig. 2). Treatment with tannic acid led to significant alterations in the expression levels of several key apoptotic genes in PC-3 cells (Fig. 2). Among the down-regulated genes, the expression of ATM, BCL2, BCL2A1, BIK, BIRC2, BIRC3, BRE, CASP3, CASP6, CASP8, CHEK2, CRADD, PPIA, RPA3, TNFSF18, TRAF1, TRAF2, TRAF4, and TRAF5 was significantly reduced compared to the untreated cell line (p < 0.05). These genes play essential roles in various apoptotic pathways (20) , and their down-regulation may contribute to the anticancer effects of tannic acid in PC3 cells. Conversely, tannic acid treatment resulted in the up-regulation of DAPK1, TNF, TNFRSF10C, TNFRSF1A, TNFRSF8, TNFSF11, TNFSF15, and TP73L as compared to the untreated cell line (p < 0.05). Notably, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and its receptor TNFRSF1A were highly up-regulated (p < 0.001), indicating that the TNF signaling pathway might be involved in the response to tannic acid treatment. Additionally, DAPK1, which is known to promote apoptosis, exhibited a substantial increase in expression (p < 0.001), further supporting the pro-apoptotic effects of tannic acid.
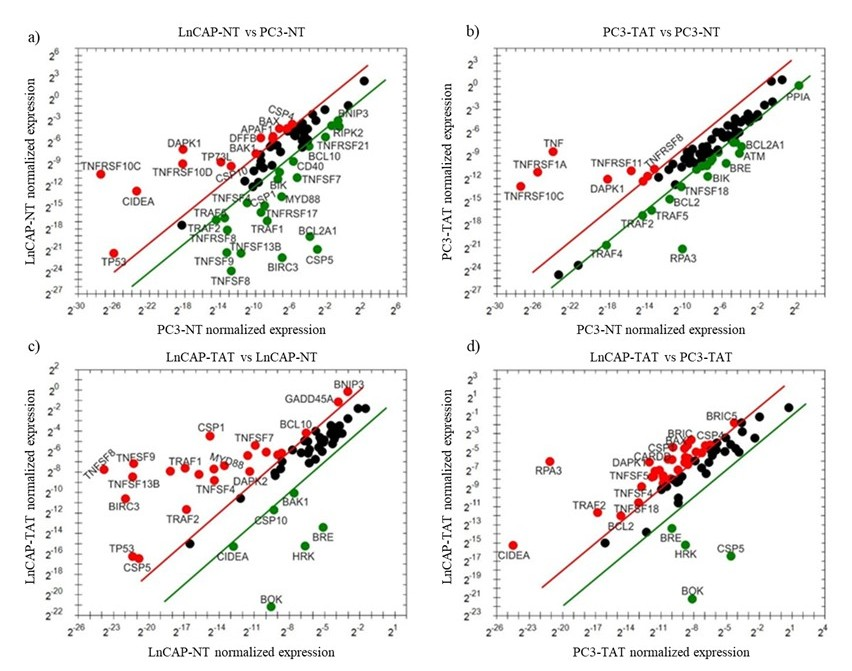
Fig. 2. Comparison of normalized expression of genes involved in the apoptotic pathway. The scatter plots were drawn by GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, California; Version 8.4.3). The X- and Y-axis represent relative gene expressions normalized to the internal standard control for each cell line. The red and green dots represent the up-regulated and down-regulated genes, respectively. Black dots represent genes that do not show a statistically significant change; lower than 2-fold. a) Comparison of gene expression of non-treated LnCaP and PC-3 cells, b) Comparison of gene expression of tannic acid-treated PC-3 cells with and non-treated PC-3 cells, c) Comparison of gene expression of tannic acid-treated LnCaP cells with and non-treated LnCaP cells, and d) Comparison of gene expression of tannic acid-treated LnCaP cells with and tannic acid-treated PC-3 cells.
Treatment with tannic acid also elicited significant changes in the expression levels of various apoptotic genes in LnCaP cells (Fig. 2). BAK1, BOK, BRE, CASP10, CIDEA, and HRK expressions were significantly decreased compared to the untreated cell line ( p < 0.05), suggesting that their downregulation, known to play vital roles in promoting apoptosis and maintaining cellular homeostasis, may contribute to the altered apoptotic response induced by tannic acid in LnCaP cells. On the other hand, tannic acid treatment resulted in the up-regulation of multiple genes involved in apoptotic signaling. The expressions of BCL10, BIRC3, BNIP3, CASP1, CASP5, CD40, CIDEB, DAPK2, FASLG, GADD45A, MYD88, RPA3, TNFRSF10D, TNFRSF17, TNFRSF8, TNFSF13B, TNFSF4, TNFSF7, TNFSF8, TNFSF9, TP53, TRAF1, and TRAF2 were significantly increased compared to the untreated cell line ( p < 0.05). These up-regulated genes have diverse functions in apoptotic pathways, such as regulation of caspases, TNF receptor signaling, and activation of pro-apoptotic factors, indicating that tannic acid treatment can potentially induce a robust apoptotic response in LnCaP cells.
The relative normalized expression of each gene was compared to the regulation threshold to determine whether the genes were up-regulated or down-regulated upon tannic acid treatment. Up and down-regulated gene clusters involved in the apoptosis pathway of PC-3 and LnCAP cells were summarized in Fig. 3.
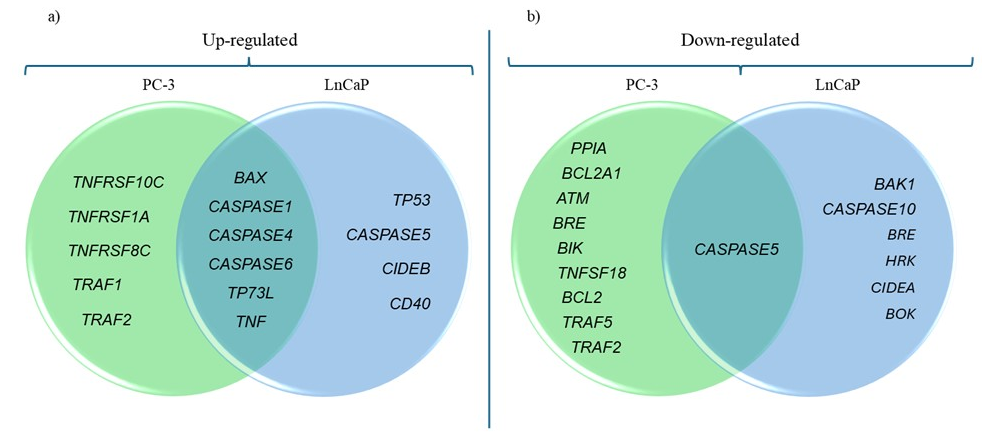
Fig. 3. a) Up- and b) down-regulated genes after tannic acid treatment. The green and blue circles represent PC-3 and LnCaP cells, respectively.
The comparison between PC3 and LnCaP cells treated with tannic acid highlights both common and distinct alterations in apoptotic gene expression. For example, in both PC3 and LnCaP cells treated with tannic acid, the expression levels of several genes including ATM, BCL2, BCL2A1, BIK, BIRC2, BIRC3, BRE, CASP3, CASP6, CASP8, CHEK2, CRADD, and RPA3 were down-regulated whereas the expression of DAPK1, TNF, TNFRSF10D, TNFRSF17, TNFRSF8, TNFSF13B, TNFSF4, TNFSF7, and TNFSF8 was up-regulated compared to the untreated cell line. The common down-regulation of anti-apoptotic genes and up-regulation of pro-apoptotic genes in both cell lines suggest that tannic acid treatment may generally promote apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. This indicates its potential as a broad-spectrum therapeutic agent for inducing apoptosis in different prostate cancer subtypes. The expression level of PPIA and TNFSF18 was down-regulated in PC3 cells treated with tannic acid, while in LnCaP cells, the expression level of BOK, CIDEA, and HRK was down-regulated. When we examine the genes that were up-regulated in both cell lines, the expression of TP73L and TRAF1 was up-regulated in PC3 cells, while in LnCaP cells, the expression of BCL10, BIRC3, BNIP3, CASP1, CASP5, CD40, CIDEB, MYD88, and TRAF2 was up-regulated. The differences observed in the gene expression profiles between PC3 and LnCaP cells indicate that tannic acid's apoptotic effects might be cell-type specific. These differences may arise from variations in the genetic background and molecular characteristics of the two cell lines (21) . It suggests that tannic acid's efficacy as an apoptosis-inducing agent may vary depending on the specific prostate cancer subtype, and its mechanisms of action might involve distinct apoptotic pathways in different cell types. These findings highlight the significance of comprehending the molecular heterogeneity of prostate cancer and customizing therapeutic approaches accordingly.
The results provide valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying the anticancer effects of tannic acid in prostate cancer cells. The observed alterations in mRNA expression of apoptotic genes suggest that tannic acid treatment can modulate key signaling pathways involved in apoptosis, thereby influencing cell survival and death in PC3 and LnCaP cells. The down-regulation of various anti-apoptotic genes in PC3 cells, such as BCL2, BCL2A1, and members of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family (BIRC2 and BIRC3), may promote apoptosis by reducing the inhibitory signals that prevent cell death. The observed down-regulation of pro-apoptotic genes in LnCaP cells, such as BAK1, BOK, BRE, and HRK, suggests that tannic acid may interfere with key regulators of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, which is controlled by members of the BCL2 family. The decreased expression of CASP3, CASP6, and CASP8 in PC3 cells indicates a potential inhibition of caspase-mediated apoptotic pathways, which are crucial for executing the apoptotic program (22) whereas decreased expression of CASP10 in LnCaP cells, a caspase involved in the extrinsic apoptotic pathway (23, 24), indicates a potential impairment in death receptor-mediated apoptosis in response to tannic acid. Conversely, the up-regulation of pro-apoptotic genes such as DAPK1, TNF, and members of the TNF superfamily ( TNFRSF10C, TNFRSF8, TNFSF11, and TNFSF15) in PC3 cells indicates an active promotion of apoptosis by tannic acid. The up-regulation of TNF and its receptors suggests that the TNF signaling pathway might be a significant mediator of tannic acid-induced apoptosis in PC3 cells. The up-regulation of various apoptotic genes in LnCaP cells treated with tannic acid underscores its potential as a pro-apoptotic agent. The increased expression of CASP1, CASP5, and other caspases supports the activation of caspase-mediated apoptosis upon tannic acid treatment. The elevated expression of BCL10, an activator of the canonical NF-κB pathway (25), might contribute to the induction of apoptosis through the TNF receptor signaling pathway. The up-regulation of TNF-related ligands ( TNFSF4, TNFSF7, TNFSF8, TNFSF9, TNFSF13B) and their receptors ( TNFRSF10D, TNFRSF17, TNFRSF8) indicates potential involvement of death ligand-receptor interactions in mediating apoptosis. The up-regulation of TP53 (p53), a critical tumor suppressor and a key regulator of apoptosis (5, 24), further strengthens the pro-apoptotic effects of tannic acid. The activation of TP53 can lead to the transcription of pro-apoptotic target genes, promoting cell death in LnCaP cells. Overall, the significant alterations in the expression of apoptotic genes in response to tannic acid treatment support its potential as a therapeutic agent for inducing apoptosis in PC3 and LnCaP cells. These findings contribute to our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the pro-apoptotic effects of tannic acid in prostate cancer cells. However, further investigations, including functional assays and in vivo studies, are required to fully elucidate the specific apoptotic pathways modulated by tannic acid and to evaluate its potential as a targeted therapy for prostate cancer.
In a study by Nagesh et al. (26), the effects of tannic acid on prostate cancer cells were explored at the protein expression level. They observed that treatment with tannic acid for 24 hours induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in the cells. This stress resulted in a decrease in the expressions of PERK and IREα, as well as anti-apoptotic proteins BCL2 and BCLXL. Conversely, pro-apoptotic proteins BAX and BAK were found to be upregulated. Moreover, the expression of cleaved caspase-3 and fragmented PARP proteins increased, promoting apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Further investigations in PC-3 cells revealed an increase in pro-apoptotic BAX and a decrease in anti-apoptotic BCL2A1 expression following tannic acid treatment (4). The upregulation of caspase-8 supported mitochondrial stress in the cells, subsequently activating caspase-9 through stimulation of procaspase-9 by CytC and Apaf-1. Caspase-9 expression triggered apoptosis by cleaving substrates with caspase-3 and caspase-6 (27–29). Endoplasmic reticulum stress also activated the calcium signaling pathway, stimulating caspase-3 and caspase-7 (30, 31). These stimuli suppressed PARP and ICAD genes, leading to apoptosis triggered by reduced poly (ADP-ribose) synthesis and DNA fragmentation (32, 33). Additionally, tannic acid-induced oxidative stress in cancerous cells resulted in DNA damage. This led to an increase in gene expression, particularly TP53, involved in the signaling and repair mechanism. The increased gene expression further activated pro-apoptotic BAX, BAK, and APAF1 genes, ultimately promoting apoptosis.
In the future application of our study findings in therapy, the potential use of tannic acid as a therapeutic agent for prostate cancer treatment emerges as a promising avenue. The data obtained from our study shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying tannic acid-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells, indicating its potential efficacy in targeting prostate cancer. The observed apoptosis triggered by both mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum stress, along with the modulation of TNF receptors and associated genes, TRAF1, TRAF2, and GADD45, underscores the multifaceted impact of tannic acid on prostate cancer cells. These findings suggest that tannic acid can intervene in crucial signaling pathways involved in apoptosis regulation, making it a compelling candidate for therapeutic intervention. Furthermore, the significant alterations in the expression of apoptotic genes, including the down-regulation of anti-apoptotic genes and the up-regulation of pro-apoptotic genes, further support the therapeutic potential of tannic acid in prostate cancer treatment. By targeting key players in apoptotic pathways, tannic acid demonstrates its ability to induce apoptosis in prostate cancer cells, potentially leading to tumor suppression. Moving forward, it is imperative to conduct further studies, including in vivo investigations, to validate the efficacy and safety of tannic acid as a therapeutic agent for prostate cancer patients. These studies will provide a deeper understanding of the precise mechanisms by which tannic acid induces apoptosis and will help elucidate its potential as a targeted therapy for prostate cancer.
CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, our study demonstrates that tannic acid exerts potent anticancer effects in prostate cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. Treatment with tannic acid led to significant changes in the expression of apoptotic genes, both in PC-3 and LnCaP cells. The down-regulation of anti-apoptotic genes ( e.g., BCL2, BCL2A1) and up-regulation of pro-apoptotic genes ( e.g., DAPK1, TNF) indicate its ability to modulate key signaling pathways involved in apoptosis. Moreover, tannic acid treatment activated both mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum stress, leading to the induction of apoptosis through various apoptotic pathways. The findings suggest that tannic acid holds promise as a potential therapeutic agent for prostate cancer treatment, with the ability to target different prostate cancer subtypes. Further studies, including in vivo investigations, are needed to fully understand the precise mechanisms of tannic acid-induced apoptosis and to evaluate its potential as a targeted therapy for prostate cancer patients. Overall, our findings highlight the significance of tannic acid as a potential adjunct treatment for the management of prostate cancer.
Conflicts of interest. – The authors declare no competing interests.
Funding. – This study was supported by the Research Foundation of Selçuk University, Turkiye (Grant numbers: 16401114, 19401099).
Authors contributions. – Conceptualization, Se.K. and Ç.G.-S.; methodology, Ç.G.-S., Si.K. and Se.K.; analysis Ç.G.-S., Si.K. and Se.K.; writing, original draft preparation, Ç.G.-S. and Se.K.; writing, review and editing, Ç.G.-S. and Si.K.; funding acquisition and project administration, Se.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
