1. INTRODUCTION
Researchers have reported on the potential ecological impacts that wildlife tourism can have on dolphins, the risks to people, and the economic benefits to local communities (e.g.Newsome, Dowling and Moore 2005;Orams 2002;Patroni, Simpson and Newsome 2018a;Senigaglia et al. 2016;Wilson and Tisdell 2003). The literature however contains fewer studies into the social aspects (human dimensions) of dolphin tourism such as visitor satisfaction and the attitudes of participants (Patroni 2018;Patroni et al. 2018a). Social aspects are an important consideration in any management strategy to keep wild dolphin tourism operations sustainable by balancing the welfare of the dolphins with the desires and expectations of tourists in their interactions with these charismatic iconic marine mammals (Bach and Burton 2017;Newsome, Moore and Dowling 2013;Sotiriadis 2017). Each wildlife tourism operation is unique and requires a management approach adapted to the species, location, and participant desires (Dubois and Fraser 2013). Hereafter in this communication, tourists and local residents who interact with wild dolphins in marine environments in regulated or unregulated tourism experiences are referred to as visitors.
This communication provides an overview of recent literature related to visitor satisfaction with dolphin tourism experiences. Further, we highlight the importance of understanding human aspects, such as visitor attitudes to dolphin welfare and environmental education. The literature regarding the impacts of tourism on dolphin welfare, the benefits that are derived from dolphin tourism, and management techniques employed to ensure a sustainable dolphin tourism operation are also explored.
2. WILD DOLPHIN TOURISM
Many visitors in search of nature-based experiences are attracted to coastal and marine destinations for wildlife tourism experiences, as these productive habitats support a great diversity of species, including many that are charismatic and of appeal to visitors (Gier, Christie and Amolo 2017;Newsome et al. 2013;Patroni 2018;Schleimer et al. 2015). Such areas often enhance their destination image by offering a range of recreational activities such as scuba-diving, snorkelling, and boat tours that provide the opportunity for visitors to view marine wildlife in their natural habitats (Madden, Rashid and Zainol 2016;Newsome et al. 2013). Dolphins are highly regarded by humans and are one of the most popular targets for wildlife tourism experiences (Curtin 2005; Orams1995 and1997;Smith et al. 2006b). Interest in wild dolphins has given rise to different types of experience being offered including: swimming with dolphins, boat tours, and up-close beach-based viewing experiences (Orams 1995;Wiener 2013;Peters et al. 2013;Patroni 2018). The viewing of animals in the wild however is not guaranteed and tends to rely on chance encounters, with the possibility of leaving visitors dissatisfied when their expectations of interacting with wildlife are not met.
2.1. Visitor Motivation for Dolphin Interactions
The human dimensions of dolphin tourism vary greatly from other marine wildlife tourism experiences, in part because dolphins have held great appeal to humans for a long time, and are widely considered as being among the most charismatic wildlife (Barney, Mintzes and Yen 2005;Besio, Johnston and Longhurst 2008).Curtin (2006) reported that participants felt their dolphin experience improved their physical and emotional wellbeing and that the dolphins appeared to enjoy the interaction and be smiling, which can be interpreted as anthropomorphism of the dolphins.Webb and Drummond (2001) also reported therapeutic benefits, and the lifting of the human spirit as a result of interacting with dolphins.Taylor (2003) andAntonioli and Reveley (2005) further suggested that swimming with dolphins can alleviate depression or illness. Several authors have considered the justification for some animal species being more sought after than others, withFreeman and Kreuter (1994) andSmith et al. (2006a) suggesting that humans connect with the playfulness, curiosity, and social habits of dolphins and their apparent desire to interact with humans, which mirrors attributes present in humans themselves (Zeppel and Muloin 2008a). Furthermore, dolphins are aesthetically pleasing to humans, give off a graceful and agile sense of movement, and the sounds of their communication appeal to humans (Wiener 2015).
McIntosh and Wright (2017) andCater and Cater (2007) also describe the attraction of wild dolphin experiences reporting that visitors to marine mammal experiences desire a psychological benefit and emotional connection, which makes close proximity with the target species and species relatability important elements for the wildlife tourism operation. The same authors also suggest that this emotional and perceived connection can be gained through connecting in a ‘human way’ with dolphins, including eye contact, which gives the human participants a sense of acknowledgement and connection. Additionally,Cater and Cater (2007) suggested visitors interpret the curve of a dolphin rostrum as a smile, giving the impression the dolphin is enjoying the interaction and also feeling some sort of emotional connection. Supposed signs of engagement from the dolphins are easily misinterpreted and visible signs of stress may be undetected or misinterpreted as playful behaviour. For example, while eye contact is a form of communication or connection between humans, many animals, including dolphins, perceive eye contact as threatening, so the assumption in the mind of the visitor that dolphins use the same social cues creates a misunderstanding that is potentially harmful and hazardous to dolphins and humans alike (Curtin 2006;Desmond 1999;Wiener 2013).
Treating dolphins in a human manner arises from the expectations visitors have for the experience. Dolphins have long been romanticised as friendly caring creatures, not only by their mannerisms, but also by the way they are portrayed in popular culture and how captive dolphins have been trained to behave (Wiener 2015). The perceptions humans have of dolphins can influence the way visitors behave in their presence, whichWiener (2015) found was without a great deal of awareness or caution.Wursig and Wursig (2003) argue that these interactions require the exertion of energy that could be better expended into necessary life processes of the dolphins, even when dolphins participate out of their own free will and humans interpret the interactions as shared enjoyment.
2.2. Attitudes and Satisfaction with Dolphin Tourism
Visitor satisfaction is a vital component of dolphin tourism experiences (Newsome et al. 2013;Patroni 2018;Patroni et al. 2018a). Visitor satisfaction is the ability for an experience to meet the expectations and desires of visitors, which are often formulated before the actual experience takes place (Soldić Frleta 2014). Ensuring an experience meets visitor expectations increases the likelihood that visitors will return or become regular visitors and they may recommend the experience to others through word-of-mouth and online sharing of their positive (or negative) experiences (Chen and Segota 2015;Lai and Vinh 2013;Madden et al. 2016;Prakash et al. 2018). This is important, as tourist operations rely on income from visitors to ensure they can keep operating (business viability) and providing the wildlife tourism experience (Gier et al. 2017;Schleimer et al. 2015;Soldić Frleta 2018;Wilson and Tisdell 2003). Understanding the satisfaction of visitors also provides an indication of what is working well and what can be improved in order to keep visitors satisfied and further improve offerings to better compete with other operators offering similar experiences (Soldić Frleta 2014;Smolčić Jurdana and Soldić Frleta 2011;Taplin 2012).
While the majority of visitors who engage in dolphin experiences are highly satisfied, some surveys have highlighted public concern for the welfare and health of the dolphins. Participants in the study ofSitar et al. (2017) reported that the most important aspects of dolphin watching experiences were: receiving education about the dolphins; having the tour company follow codes of conduct to minimise harm to dolphins; and having the appropriate licencing. Similarly, responses to a questionnaire byFilby, Stockin and Scarpaci (2015) reported visitors are unsatisfied when tour operators did not follow codes-of conduct. At the same time, these concerns may conflict with the strong desire of visitors for an up-close experience. For example, the survey ofBach and Burton (2017) on the trade-offs visitors were willing to make between dolphin welfare and dolphin interaction at Monkey Mia in Western Australia reported that visitors were willing to pay more to gain close proximity to the dolphins. While the Monkey Mia visitors placed greatest emphasis on the predictability and proximity to dolphins, 80% were however willing to accept decreased time and proximity, if the benefits to dolphin welfare were clearly communicated.Filby et al. (2015) also found that visitors reported the most important aspects of a dolphin-swim tour was observing dolphins in their natural environment; opportunity to see dolphins; and knowledgeable staff (Filby et al. 2015). Seeing large numbers of dolphins and being in close proximity were both ranked last as reasons for visitors taking a swim tour.Aragones et al. (2013) explored visitor perceptions of dolphin watching and found that 67% were satisfied with the overall quality of tours, as they got to watch groups of dolphins in close proximity within their natural environment for a practical price, while approximately 91% of visitors indicated the need for a ‘Special Management Plan’ focusing on the protection of cetaceans and their habitats.
Similarly, the pilot study ofSimpson, Newsome and Day (2016) and the more comprehensive confirmatory study byPatroni (2018) conducted in Bunbury, Western Australia found that, overall, visitors: were knowledgeable about the potential negative impacts of tourism on wild dolphins; supported/were satisfied with their experience at the Dolphin Discovery Centre (DDC) beach-based interaction with the local wild dolphin population; indicated the importance of having knowledgeable staff/volunteers; and expressed a desire to be informed/educated about the dolphins and associated conservation and research work of the DDC and Murdoch University.
3. FEEDING WILD DOLPHINS FOR TOURISM
To increase the chance of a sighting of marine wildlife in their natural environment, tourism operators often use provisioning as a tool to encourage proximity and predictability for wild dolphin experiences (Newsome et al. 2005;Patroni et al. 2018b;Orams 2002). The acceptability of feeding of wildlife for tourism is however a contentious practice with many differing opinions as to what constitutes best practice management (Lewis and Newsome 2003;Patroni et al. 2018a;Semeniuk et al. 2009). The use of provisioning aims to meet the desires and expectations of visitors for an up-close wildlife interaction.
Feeding of dolphins for tourism is controversial. There is currently no consensus regarding the sustainable management of such experiences and different management strategies and regulations are applied at different sites (Newsome and Rodger 2008;Newsome and Rodger 2013;Orams 1997;Patroni et al. 2018b). While these experiences provide visitors with the up-close interaction they desire, the negative impacts to dolphins can be numerous (see Section 4.0). As dolphins are social animals, many aspects of their natural behaviour can be interrupted by the impacts of tourism (Orams 2002;Scarpaci, Nugegoda and Corkeron 2010;Steckenreuter, Möller and Harcourt 2012). A conceptual model for the tensions associated with the feeding of wild dolphins for tourism is provided byFigure 1.
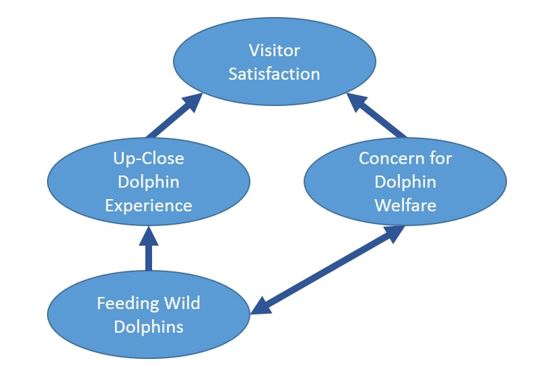
Source:Patroni (2018)
Visitors who feed dolphins as part of a visitor experience that lacks an educational component about the potential negative impacts and illegality of feeding wildlife without a licence may try to seek out opportunistic experiences and interact with wild dolphins on their own terms. In addition, understanding when feeding is and is not acceptable can be complicated by differing tourism scenarios and policies (Newsome and Rodger 2008;Newsome and Rodger 2013). This can lead to unregulated feeding in which visitors seek the up-close experience with wild dolphins outside of managed tourism experiences. This can occur when fishing vessels or recreational boats encounter dolphins. Such unmanaged/unregulated encounters may then lead to negative impacts (Constantine 1999;Donaldson et al. 2012;Markwell 2015;Newsome et al. 2005). Unregulated feeding, which often accompanies private boat-based engagement with wild dolphins, is known to result in negative impacts (Patroni et al. 2018a).
4. DOLPHIN WELFARE
Wildlife tourism can produce social, economic, and conservation benefits, however, many studies report negative impacts on the health and behaviours of target species that arise from tourism in general and wild dolphin tourism more specifically, in particular those experiences that incorporate wildlife feeding (Newsome et al. 2005;Patroni, 2018; Patroni et al.2018a and2018b;Senigaglia et al. 2016). When compared to terrestrial wildlife tourism, marine wildlife is exposed to additional impacts, which for dolphins can include collisions with boats, water quality decline, and being caught as bycatch or entangled in equipment as habituation attracts targeted wildlife to the presence of humans and their vessels (Murray et al. 2016;Orams 2002;Patroni et al. 2018a). Furthermore, the research into marine wildlife tourism tends to be focused on the ecological impacts of tourism on charismatic and iconic animals such as whales and dolphins, which are of great interest to both visitors and tourism industry stakeholders (Gallagher and Hammerschlag 2011;Smith et al. 2008;Vianna et al. 2012).
4.1. Impacts of Tourist Boat Traffic
The time spent resting, feeding, and socialising are important activities for reproductive success in dolphins (Peters et al. 2013). One of the most commonly studied impacts of human-dolphin interactions concerns how boat traffic associated with dolphin watching and swim-with experiences affects the time wild dolphins spend foraging (Dans et al. 2008;Meissner et al. 2015;Scarpaci et al. 2010;Wiener 2015). The contradictory studies ofSteckenreuter et al. (2012) andTrone, Kuczaj and Solangi (2005), among others, illustrate the complexity of studying the impacts that arise due to interactions between wild dolphins and tourist boats.
Steckenreuter et al. (2012) reported that wild dolphins displayed a reduced activity budget in the presence of boats that was influenced by the number of boats present. During their study, the time dolphins spent feeding decreased by 66%, time spent socialising decreased by 44% and the dolphins also exhibited reduced resting time. In contrast,Trone et al. (2005) found no short or long-term changes in dolphin behaviour. The only behaviour changes they reported was the amount of time spent playing, and that increased with human interaction. Other studies have however reported that dolphins change their typical range or group cohesiveness in order to avoid areas where vessels are operating (Bejder et al. 2006;Peters et al. 2013). The noise of tourism vessels has also been reported to interrupt and override the communication between dolphins and other biologically important sounds (Luís, Couchinho and Santos 2014;Pine et al. 2016;Sims, Hung and Wuersig 2012). However, this is countered by the study ofPine, Wang and Wang (2016) who reported feeding activity by dolphins was not affected by the presence of vessel noise.
4.2. Impacts of Swimming with Wild Dolphins
Swimming with dolphins is one of the most desired dolphin experiences.Wiener (2015) proposes that swimming alongside a dolphin enhances the emotional connection and is more intimate than a birds-eye view, fulfilling the human desire for such emotional connections. However, swim-with experiences can also have direct negative impacts on wild dolphins (Bearzi 2017;Peters et al. 2013). Experiences where people swim with dolphins may be associated with the activities of a commercial operator on a regulated or unregulated basis or may be the result of visitors to marine destinations seeking out and swimming with dolphins on their own terms (Curtin 2006;Samuels, Bejder and Heinrich 2000;Spradlin et al. 2001). Furthermore, the level of impact is influenced by whether the interaction is active, with humans approaching the dolphins by swimming or using watercraft, or passive where the humans wait in the water for the dolphins to approach or not (Bearzi 2017).
Many of the impacts previously reported also arise directly as a result of swim-with dolphin experiences with reported impacts that include disturbed social behaviours, fewer and/or shorter periods of rest, lower reproductive success, and reduced foraging effort (Bearzi 2017;Filby et al. 2015;Peters et al. 2015;Samuels et al. 2000).
Of particular concern is the desire of humans to touch dolphins they are swimming with in order to feel fully connected and fulfilled by the experience (Curtin 2006;Wiener 2015). In addition to the increased physical risk to both humans and dolphins discussed in the following section, such direct contact also provides the opportunity for the two-way transfer of diseases and parasites (Bearzi 2017).Wiener (2016) notes that despite anecdotal evidence of wild dolphins being touched during swim experiences there is a lack of detail regarding these interactions in the published literature, despite a number of researchers alluding to the practice in their research (e.g.Cater and Cater 2007;Curtin 2006;Wiener 2015). We are similarly unaware of research that specifically analyses and reports on humans actually touching dolphins in the wild, butFigure 2 provides two examples of the anecdotal evidence of dolphin touching that is available online as images and videos shared through social networking sites. The upper image is from the video of an interaction near a beach in Sydney, Australia that shows a group of swimmers, accompanied by scuba divers with cameras, touching a dolphin with their hands and feet during a coordinated, but most likely unregulated, swim experience. The lower image is from a video shared online by one of two jet-ski riders from Florida, USA who on their own terms located, swam with, and touched a wild dolphin.
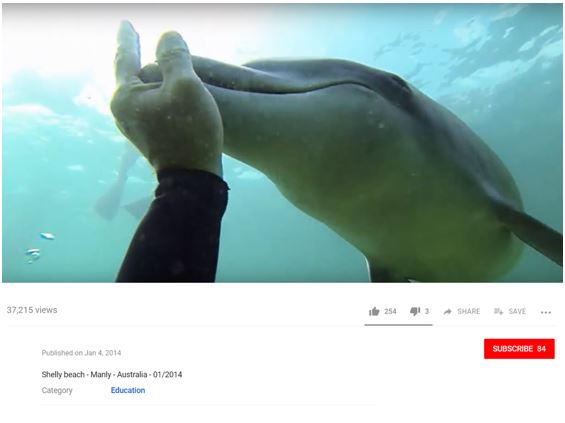
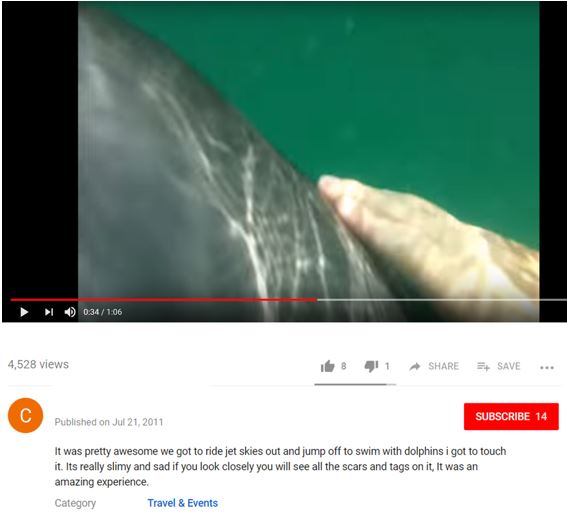
Source: Still images from videos shared on YouTube viewed on 24 October 2018.
4.3. Impacts of Wild Dolphin Feeding
The provisioning of food to encourage wild dolphins to come into close contact with visitors is commonly used by tour operators to enhance the visitor experience and satisfaction (Bach and Burton 2017;Orams 2002; Patroni et al.2018a and2018b). Despite the practice generally being illegal, it is also common for members of the general public to feed wild dolphins for the same reason (Christiansen et al. 2016;Hazelkorn Schulte and Cox 2016;Patroni 2018;Patroni et al. 2018b). Some, if not most, regulated feeding activates arose out of cooperative fishing activates between dolphins and humans and/or casual/illegal feeding of wild dolphin (O'Neill, Barnard and Lee 2004;Orams 1995). Such feeding can however have implications for the welfare and natural behaviours of the dolphins.
Dolphins are intelligent animals living and existing in social groups and tourism activities can disturb these social behaviours, group relationships, and communications (Orams 1997;Newsome et al. 2013). Several studies report on the impacts of feeding wild dolphins.Foroughirad and Mann (2013) for example report that female dolphins provisioned for tourism have reduced levels of parental care for their calves and ultimately a higher calf mortality rate. Those authors also reported that even with reduced levels of provisioning, calf behavioural development was impacted. In contrast, a study on calf survival rates at a provisioning site in Tangalooma found that calf survival was 100%, even for orphaned calves (Neil and Holmes 2008).Neil and Holmes (2008) hypothesised this outcome to be the product of the isolated location and high-water quality in combination with the controlled management routine that limits duration of the tourism interactions and provides quality fish as a food source (Neil and Holmes 2008).
Many authors describe the impacts of feeding on the social behaviour of wild dolphins, which are ecologically important as dolphins feed and live in social groups, and it has been reported that some provisioned dolphins have even become solitary animals (Dans et al. 2008;Orams 1997;Scarpaci et al. 2010).
Dolphin feeding for tourism also affects dolphins physically, with feeding leading to dolphins becoming conditioned to humans and therefore having a higher risk of being struck by passing vessels or getting tangled in or injured by commercial and/or recreational fishing equipment (Donaldson, Finn and Calver 2010;Hazelkorn et al. 2016). Further, such feeding practices cause the dolphins to be attracted to vessels begging for food, which both increase the amount and type of food that these dolphin are feed and creates even higher instances of dolphins being struck by boats and being entangled in fishing equipment (Christiansen et al. 2016;Donaldson et al. 2010;Hazelkorn et al. 2016).
Examples of food provisioning by tourism operators are offered by the experiences at Bunbury and Monkey Mia in Western Australia; at Tangalooma on Moreton Island and Tin Can Bay in Queensland, Australia; and at the Negro River, Brazil (Table 1). Feeding practices at each of these locations have different management strategies and regulations with differing levels of operator control and visitor participation (Bach and Burton 2017;Orams, Hill and Baglioni 1996;Smith, Samuels and Bradley 2008).
Source: Adapted fromPatroni (2018). Percentages based on minimum daily requirement of 8 kg of fish.
4.4. Risky Interactions
As for the interactions between humans and any form of wildlife, the interactions between humans and dolphins have in many cases been described as risky for the humans. As previously mentioned, the interaction of habituated dolphins with humans can, however, also be risky for the dolphins, as outlined below.
Despite the majority of visitors to controlled dolphin interactions expressing their concern for the welfare of the dolphins (Aragones et al. 2013;Bach and Burton 2017;Patroni 2018), there are several reported cases of dolphins being both accidentally and deliberately harmed and killed by humans (Orams 1997;Samuels et al. 2000;Wells at al. 2013). Hence, monitoring and enforcement to prevent illegal human-dolphin interactions is a crucial element for effective management of wild dolphin populations targeted for tourism (Orams 1997;Machernis et al. 2018).Patroni (2018) reported strong community support for such enforcement action to protect the safety and welfare of the resident wild dolphin population at Koombana Bay, Bunbury.
Dolphins are wild animals that can be unpredictable and dangerous, despite the common perception of dolphins being friendly and playful animals (Cong et.al. 2017).Orams et al. (1996) refers to circumstances in which dolphins have become ‘pushy’, precipitating forceful contact with humans during feeding at Tangalooma.Orams (1997) also describes cases of people being dragged out to sea and of divers being held under water.Smith et al. (2008) suggested that dolphin aggression at Tangalooma increases with longer wait time before feeding, because of increased competition between the dolphins, especially among males. Excessive touching by humans is also thought to aggravate this behaviour.Finn, Donaldson and Calver (2008) andOrams (1997) indicate that provisioned dolphins become accustomed to humans and can be the initiators of contact and harass people, expecting food or wanting to engage in playful behaviours.
Hence, while dolphins are viewed as gentle friendly creatures, people have been injured and killed by wild dolphins and for this, and other reasons regarding dolphin welfare, feeding has been officially banned in the United States of America (USA), New Zealand and the United Kingdom (Orams 1997,Finn et al. 2008). There is evidence from the USA however that both operators and the general public continue the illegal feeding to facilitate close interactions with wild dolphins (Machernis et al. 2018). Despite extensive searching of peer reviewed databases, we could find no evidence of recent research into illegal feeding by operators and or the general public in either the United Kingdom or New Zealand, nor for the feeding of wild dolphins in Europe more broadly.
5. SOCIOECONOMIC BENEFITS
In addition to the satisfaction derived by visitors who are able to interact with wild dolphins in their natural environment, tour operators and local communities benefit greatly from dolphin tourism, as it provides income to the community, job opportunities and increases tourist visitation through personal and electronic (online) word of mouth (Bearzi 2017;Gier et al. 2017;Schleimer et al. 2015;Wilson and Tisdell 2003). These benefits are regarded as important for small towns or developing communities, as such locations tend to rely heavily on income from tourism to support local business (Mustika et al. 2012;Sumanapala et al. 2018). For example, dolphin watching in Indonesia brings in around 37,000 tourists a year and contributes a minimum of 46% of the total direct expenditure for accommodation, transport and food and beverage at dolphin tourism destinations (Mustika et al. 2012). The Scottish and in remote coastal areas of Scotland up to 12% of the local income came from the cetacean tourism industry that includes dolphin watching and swim with experiences (Newsome et al. 2005;Parsons et al. 2003).Parsons et al. (2003) also highlighted that non-consumptive cetacean tourism in rural, coastal communities of Scotland had a value three times greater than that of the commercial whaling in similar communities in Norway. This clearly demonstrates that dolphin conservation has an economic value.
Similarly, the DDC, which was the site of the research byPatroni (2018) reported in this communication, makes a significant contribution to economic and social sustainably in the regional city of Bunbury (Fenech 2011;Patroni et al. 2018b; Ball referenced in “Murdoch Researchers” 2019). In the Mediterranean climate of southwest Western Australia (SWWA), the peak visitation period occurs between October and April (Simpson 2011; Simpson et al. 2016;Patroni et al. 2018b). In this highly seasonal regional tourism market, the DDC is considered to be one of four iconic ecotourism attractions in SWWA and Bunbury’s single most important tourist attraction (EVOLVE Strategic Solutions 2015;Tourism WA 2007).
6. EDUCATION AND MANAGEMENT
Education and interpretation have long been discussed as important aspects of marine wildlife tourism in two main contexts. Firstly, for the encouragement of environmental awareness and positive conservation behaviours, and for spreading information and awareness to others from visitors who receive such educational experiences (Pratt and Suntikul 2016;Zeppel and Muloin 2008b). Secondly, for the satisfaction of visitors, a majority of who indicate a desire to be educated as part of their experience (Orams 1997;Sitar et al. 2017). For example,Ballantyne, Packer and Hughes (2009) report visitor support for conservation messages in wildlife tourism with over 90% of surveyed visitors agreeing or strongly agreeing they wanted to receive information about marine wildlife, conservation messages, and to know what visitors can do to protect marine wildlife. In the same study, only 26% of visitors believed that operators should let people view marine life without providing basic facts. Further,Lück (2015) examined not only the importance of this education component, but also the specific topics about which visitors were most interested to receive more information. He reported that while visitors were highly satisfied with their experience overall, the desire of many of the visitors to learn was not sufficiently met. These results show that visitors have a desire for more information about wild dolphins and the wider marine environment.
Education also promotes pro-environmental behaviour in those visitors that have been exposed to educational content and interpretation (Barney et al. 2005;Bach and Burton 2017).Aragones et al. (2013) demonstrated how visitor and stakeholder opinions and discussions can be used in a participatory management process, which resulted in the formation of an association for dolphin and whale tourism operators and the eventual production of cetacean watching protocols in the Philippines. Combining this participatory process with monitoring, visitor information, and stakeholder involvement assisted greatly in the management of cetacean tourism in the southern Tanon Strait, Philippines.
Filby et al. (2015) suggests that education of visitors could even assist in situations where tour operators may break codes of conduct in order to increase perceived visitor satisfaction by facilitating close proximity to marine wildlife. As most visitors are happy to comply with regulations and do not want to impact dolphins negatively,Filby et al. (2015) proposed that with appropriate education visitors can even direct operators towards increased compliance. Visitors can thus be encouraged to act in accordance with management practices. This may also facilitate tour operator compliance with established codes of conduct. This in turn would take the pressure off operators to deliver ‘up-close’ experiences as visitors themselves would be more understanding of the rules regarding interactions with wildlife. Several other studies also report on the ability of environmentally aware visitors to influence how wildlife tourism operations are managed by holding operators to appropriate standards or codes of practice and by the general public raising concerns about and/or reporting dolphin threatening behaviour (e.g.Ballantyne et al. 2009;Barney et al. 2005;Bach and Burton 2017).
Wiener (2015) supports the view that educating visitors about the harm that inappropriate interactions may cause benefits dolphin welfare by improving the environmental behaviours and modifying the expectations of those who participate in authentic dolphin-based wildlife tourism experiences. Increasing the level of awareness and potential changes in behaviour also has the ability to reduce instances of unregulated interactions by the general public, as most people do not want to endanger the welfare of the dolphins (Ardoin et al. 2015;Barney et al. 2005;Smith et al. 2008). The touching of dolphins that we reported earlier could potentially be addressed through the educative component of dolphin tourism experiences by modifying visitor perceptions and overcoming the human instinct and desire to establish a connection through the sense of touch. Educated visitors are likely to have a greater respect for the dolphins as wild animals (Bach and Burton 2017;Barney et al. 2005;Curtin 2006;Lai and Vinh 2013).Dubois and Fraser (2013) andRodger et al. (2011) have proposed frameworks that assist in determining the appropriateness of wildlife tourism experiences based on how the interactions are controlled and managed and whether or not the experience has conservation benefits.
The framework ofRodger et al. (2011) recommends gathering information on the ecological characteristics of the target species and the environmental conditions, determining the current knowledge about the potential impacts of the wildlife tourism experience, and assessing whether processes are in place to monitor wildlife welfare and detect signs of environmental change. The framework also requires the gathering of knowledge on operational and social aspects of the experience, such as details on the nature and frequency of the interactions taking place, the educational information delivered, the expectations of visitors, and compliance with licence conditions and/or codes of conduct. Such an approach clarifies the circumstances for each individual wildlife tourism operation/experience, including both ecological and social aspects, in order to create an experience that ensures wildlife welfare alongside visitor satisfaction.
Dubois and Fraser (2013) identified that each case of feeding wildlife for tourism is unique, with the target species, site conditions, and purpose of the feeding determining the type magnitude of the impacts that occur. They then devised a framework that helps determine for what species and under what circumstances wildlife feeding is acceptable, based on the capacity for the feeding to be controlled and managed and whether or not the operation has conservation benefits. Adopting such a framework can identify cases where feeding may assist in preventing the welfare of dolphins being impacted at marine tourism destinations. Frameworks such as those ofRodger et al. (2011) andDubois and Fraser (2013) allow visitors to interact with wild dolphins in controlled, environmentally educative, well managed wildlife tourism experiences, which can provide broad conservation benefits and enhance dolphin welfare.
The long-term sustainability of dolphin tourism is dependent on integrating visitor desires and demands with resource management. Therefore it is important to understand visitor motivations for participating in a marine wildlife tourism experience, as well as their satisfaction and opinions regarding wild dolphin interactions (Bach and Burton 2017;Mlozi, Pesamaa and Haahti 2013;Sotiriadis 2017;Wiener 2015).
7. CONCLUSION
The wild dolphin tourism industry is of great value to local economies, tour operators, and the visitors who enjoy these experiences. Human attitudes towards dolphins ultimately reflect the way dolphin tourism is developed and managed and therefore it is important to understand how people experience and perceive dolphin tourism. The potential impacts that can arise from dolphin tourism need to be understood and minimised by the actions and control of tour operators and government authorities in order to make the satisfaction visitors gain from such experiences worthwhile and to ensure the long-term sustainability of wild dolphin tourism experiences. Varying management styles and differing laws and protection levels between and within countries highlights the complexity of managing human-dolphin interactions. A combined ecological and social research approach is the way forward in tackling this complexity. Furthermore, social research concerned with understanding visitor awareness, knowledge, expectations, and satisfaction has a vital role to play in developing best practice management for wild dolphin tourism experiences.
